Implications of SARS-Cov-2 infection on eNOS and iNOS activity: Consequences for the respiratory and vascular systems
- PMID: 33831567
- PMCID: PMC8021449
- DOI: 10.1016/j.niox.2021.04.003
Implications of SARS-Cov-2 infection on eNOS and iNOS activity: Consequences for the respiratory and vascular systems
Abstract
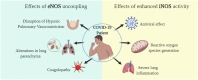
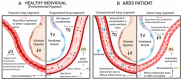
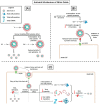
Symptoms of COVID-19 range from asymptomatic/mild symptoms to severe illness and death, consequence of an excessive inflammatory process triggered by SARS-CoV-2 infection. The diffuse inflammation leads to endothelium dysfunction in pulmonary blood vessels, uncoupling eNOS activity, lowering NO production, causing pulmonary physiological alterations and coagulopathy. On the other hand, iNOS activity is increased, which may be advantageous for host defense, once NO plays antiviral effects. However, overproduction of NO may be deleterious, generating a pro-inflammatory effect. In this review, we discussed the role of endogenous NO as a protective or deleterious agent of the respiratory and vascular systems, the most affected in COVID-19 patients, focusing on eNOS and iNOS roles. We also reviewed the currently available NO therapies and pointed out possible alternative treatments targeting NO metabolism, which could help mitigate health crises in the present and future CoV's spillovers.
Keywords: Acute respiratory distress syndrome; Antiviral effect; Coagulopathy; Coronavirus disease-19; Nitric oxide metabolism.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
New progress in roles of nitric oxide during hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Apr 14;23(14):2505-2510. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i14.2505. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28465634 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Does eNOS derived nitric oxide protect the young from severe COVID-19 complications?Ageing Res Rev. 2020 Dec;64:101201. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2020.101201. Epub 2020 Nov 4. Ageing Res Rev. 2020. PMID: 33157320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TNF/iNOS/NO pathway mediates host susceptibility to endothelial-dependent circulatory failure and death induced by betacoronavirus infection.Clin Sci (Lond). 2023 Apr 13;137(7):543-559. doi: 10.1042/CS20220663. Clin Sci (Lond). 2023. PMID: 36972169
-
The influence of renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS), endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) and erythropoietin (EPO) on COVID-19 complications.Chem Biol Interact. 2022 Feb 25;354:109834. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2022.109834. Epub 2022 Jan 26. Chem Biol Interact. 2022. PMID: 35092718 Free PMC article.
-
Human umbilical cord expresses several vasoactive peptides involved in the local regulation of vascular tone: protein and gene expression of Orphanin, Oxytocin, ANP, eNOS and iNOS.Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2011;49(2):211-8. doi: 10.5603/fhc.2011.0029. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2011. PMID: 21744319
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Effects of Inhaled Nitric Oxide Therapy in COVID-19 Patients.Biomedicines. 2022 Feb 3;10(2):369. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10020369. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35203578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Arginine in COVID-19-Induced Immunopathology and Vasculopathy.Metabolites. 2022 Mar 11;12(3):240. doi: 10.3390/metabo12030240. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 35323682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting phytoprotection in the COVID-19-induced lung damage and associated systemic effects-the evidence-based 3PM proposition to mitigate individual risks.EPMA J. 2021 Aug 3;12(3):325-347. doi: 10.1007/s13167-021-00249-y. eCollection 2021 Sep. EPMA J. 2021. PMID: 34367380 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Olive Bioactive Compounds in Respiratory Diseases.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 May 23;12(6):1140. doi: 10.3390/antiox12061140. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37371870 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Plant-Based Dietary Supplement Exhibits Significant Effects on Markers of Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Immune Response in Subjects Recovering from Respiratory Viral Infection: A Randomized, Double-Blind Clinical Study Using Vitamin C as a Positive Control.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 29;26(11):5209. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115209. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40508019 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

