Higher colorectal tissue HIV infectivity in cisgender women compared with MSM before and during oral preexposure prophylaxis
- PMID: 33831911
- PMCID: PMC8483241
- DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000002907
Higher colorectal tissue HIV infectivity in cisgender women compared with MSM before and during oral preexposure prophylaxis
Abstract
Objective: The objective of this study was to compare HIV-negative cisgender women (CGW) with MSM for mucosal tissue differences in pharmacokinetics, HIV infectivity and cell phenotype.
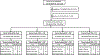
Design: A substudy of HPTN 069/ACTG A5305, 48-week study of three oral candidate preexposure prophylaxis regimens: maraviroc, maraviroc/emtricitabine and maraviroc/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) compared with a TDF/emtricitabine control group.
Methods: Plasma, peripheral blood mononuclear cells and cervical and colorectal tissue biopsies were collected at Baseline (no drug), Week 24 and 48 (on drug), and Week 49 (1-week postdrug). Drug concentrations were assessed in all matrices. HIV infectivity was assessed using tissue biopsy 'explants' challenged with HIV ex vivo followed by HIV p24 measurement. Flow cytometry evaluated colorectal cell phenotype.
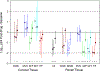
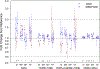
Results: Thirty-seven CGW and 54 MSM participated. CGW's colorectal explant p24 was higher than MSM before (0.31 log10, P = 0.046), during (1.01-1.19 log10, P = 0.016) and one week after (0.61 log10, P = 0.011) study drug dosing. Pooling regimens, cervical explant p24 did not differ among visits. CGW had higher plasma maraviroc and colorectal tissue tenofovir diphosphate and lower colorectal tissue emtricitabine (all P < 0.005) compared with MSM. Each study drug's cervical tissue concentrations were more than 10-fold below paired colorectal concentrations (P < 0.001). Cell phenotype sex differences included 4% higher CD38+/CD8+ cells at baseline and 3-7% higher CD69+/CD8+ cells throughout Weeks 24-49 in CGW compared with MSM (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Colorectal explants in CGW demonstrated greater HIV infectivity than MSM with and without study drugs. Small differences in adherence, drug concentration and colorectal tissue flow cytometry cannot fully explain this difference.
Copyright © 2021 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
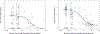
Comment in
-
Women are from venus: implications for diversified sex-based preexposure prophylaxis approaches.AIDS. 2021 Aug 1;35(10):1691-1693. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000002995. AIDS. 2021. PMID: 34270492 No abstract available.
References
-
- Thigpen MC, et al., Antiretroviral preexposure prophylaxis for heterosexual HIV transmission in Botswana. N Engl J Med, 2012. 367(5): p. 423–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UM1 AI069494/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000005/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068633/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069534/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI106707/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068617/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068619/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069419/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069424/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI045008/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069465/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068613/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050410/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068617/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

