Cholinergic suppression of hippocampal sharp-wave ripples impairs working memory
- PMID: 33833054
- PMCID: PMC8054002
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2016432118
Cholinergic suppression of hippocampal sharp-wave ripples impairs working memory
Abstract
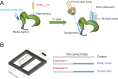
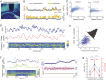
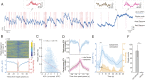
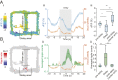
Learning and memory are assumed to be supported by mechanisms that involve cholinergic transmission and hippocampal theta. Using G protein-coupled receptor-activation-based acetylcholine sensor (GRABACh3.0) with a fiber-photometric fluorescence readout in mice, we found that cholinergic signaling in the hippocampus increased in parallel with theta/gamma power during walking and REM sleep, while ACh3.0 signal reached a minimum during hippocampal sharp-wave ripples (SPW-R). Unexpectedly, memory performance was impaired in a hippocampus-dependent spontaneous alternation task by selective optogenetic stimulation of medial septal cholinergic neurons when the stimulation was applied in the delay area but not in the central (choice) arm of the maze. Parallel with the decreased performance, optogenetic stimulation decreased the incidence of SPW-Rs. These findings suggest that septo-hippocampal interactions play a task-phase-dependent dual role in the maintenance of memory performance, including not only theta mechanisms but also SPW-Rs.
Keywords: cholinergic; hippocampus; sharp-wave ripples; theta; working memory.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Firing of Theta State-Related Septal Cholinergic Neurons Disrupt Hippocampal Ripple Oscillations via Muscarinic Receptors.J Neurosci. 2020 Apr 29;40(18):3591-3603. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1568-19.2020. Epub 2020 Apr 7. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32265261 Free PMC article.
-
Optogenetic activation of septal cholinergic neurons suppresses sharp wave ripples and enhances theta oscillations in the hippocampus.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Sep 16;111(37):13535-40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1411233111. Epub 2014 Sep 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25197052 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired spatial learning and suppression of sharp wave ripples by cholinergic activation at the goal location.Elife. 2021 Apr 6;10:e65998. doi: 10.7554/eLife.65998. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33821790 Free PMC article.
-
Septo-hippocampal signal processing: breaking the code.Prog Brain Res. 2015;219:103-20. doi: 10.1016/bs.pbr.2015.04.002. Epub 2015 May 16. Prog Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 26072236 Review.
-
Hippocampal information processing across sleep/wake cycles.Neurosci Res. 2017 May;118:30-47. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2017.04.018. Epub 2017 May 12. Neurosci Res. 2017. PMID: 28506629 Review.
Cited by
-
CA2 orchestrates hippocampal network dynamics.Hippocampus. 2023 Mar;33(3):241-251. doi: 10.1002/hipo.23495. Epub 2022 Dec 27. Hippocampus. 2023. PMID: 36575880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Topography of putative bidirectional interaction between hippocampal sharp wave ripples and neocortical slow oscillations.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 23:2024.10.23.619879. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.23.619879. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Neuron. 2025 Mar 05;113(5):754-768.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2024.12.019. PMID: 39484611 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
The effects of moderate prenatal alcohol exposure on performance in hippocampal-sensitive spatial memory and anxiety tasks by adult male and female rat offspring.Alcohol. 2024 Dec;121:75-86. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2024.08.002. Epub 2024 Aug 8. Alcohol. 2024. PMID: 39122134
-
Selection of experience for memory by hippocampal sharp wave ripples.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 8:2023.11.07.565935. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.07.565935. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Science. 2024 Mar 29;383(6690):1478-1483. doi: 10.1126/science.adk8261. PMID: 37987008 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Ultrasound-Induced Synchronized Neural Activities at 40 Hz and 200 Hz Entrained Corresponded Oscillations and Improve Alzheimer's Disease Memory.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025 Apr;31(4):e70351. doi: 10.1111/cns.70351. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025. PMID: 40202152 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buzsáki G., Two-stage model of memory trace formation: A role for “noisy” brain states. Neuroscience 31, 551–570 (1989). - PubMed
-
- Hasselmo M. E., Neuromodulation: Acetylcholine and memory consolidation. Trends Cogn. Sci. 3, 351–359 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Atri A., et al. ., Blockade of central cholinergic receptors impairs new learning and increases proactive interference in a word paired-associate memory task. Behav. Neurosci. 118, 223–236 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Coyle J. T., Price D. L., DeLong M. R., Alzheimer’s disease: A disorder of cortical cholinergic innervation. Science 219, 1184–1190 (1983). - PubMed
-
- Sitaram N., Weingartner H., Gillin J. C., Human serial learning: Enhancement with arecholine and choline impairment with scopolamine. Science 201, 274–276 (1978). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

