Adolescent fluoxetine treatment mediates a persistent anxiety-like outcome in female C57BL/6 mice that is ameliorated by fluoxetine re-exposure in adulthood
- PMID: 33833356
- PMCID: PMC8032660
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-87378-6
Adolescent fluoxetine treatment mediates a persistent anxiety-like outcome in female C57BL/6 mice that is ameliorated by fluoxetine re-exposure in adulthood
Abstract
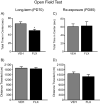
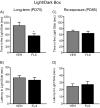
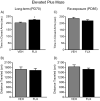
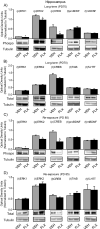
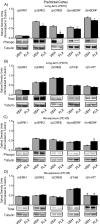
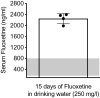
The objective of this study was to evaluate whether juvenile fluoxetine (FLX) exposure induces long-term changes in baseline responses to anxiety-inducing environments, and if so, whether its re-exposure in adulthood would ameliorate this anxiety-like phenotype. An additional goal was to assess the impact of adolescent FLX pretreatment, and its re-exposure in adulthood, on serotonin transporters (5-HTT) and brain-derived-neurotrophic-factor (BDNF)-related signaling markers (TrkB-ERK1/2-CREB-proBDNF-mBDNF) within the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. To do this, female C57BL/6 mice were exposed to FLX in drinking water during postnatal-days (PD) 35-49. After a 21-day washout-period (PD70), mice were either euthanized (tissue collection) or evaluated on anxiety-related tests (open field, light/dark box, elevated plus-maze). Juvenile FLX history resulted in a persistent avoidance-like profile, along with decreases in BDNF-signaling markers, but not 5-HTTs or TrkB receptors, within both brain regions. Interestingly, FLX re-exposure in adulthood reversed the enduring FLX-induced anxiety-related responses across all behavioral tasks, while restoring ERK2-CREB-proBDNF markers to control levels and increasing mBDNF within the prefrontal cortex, but not the hippocampus. Collectively, these results indicate that adolescent FLX history mediates neurobehavioral adaptations that endure into adulthood, which are indicative of a generalized anxiety-like phenotype, and that this persistent effect is ameliorated by later-life FLX re-exposure, in a prefrontal cortex-specific manner.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

