The cGAS-STING pathway as a therapeutic target in inflammatory diseases
- PMID: 33833439
- PMCID: PMC8029610
- DOI: 10.1038/s41577-021-00524-z
The cGAS-STING pathway as a therapeutic target in inflammatory diseases
Abstract
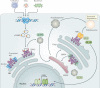
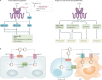
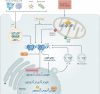
The cGAS-STING signalling pathway has emerged as a key mediator of inflammation in the settings of infection, cellular stress and tissue damage. Underlying this broad involvement of the cGAS-STING pathway is its capacity to sense and regulate the cellular response towards microbial and host-derived DNAs, which serve as ubiquitous danger-associated molecules. Insights into the structural and molecular biology of the cGAS-STING pathway have enabled the development of selective small-molecule inhibitors with the potential to target the cGAS-STING axis in a number of inflammatory diseases in humans. Here, we outline the principal elements of the cGAS-STING signalling cascade and discuss the general mechanisms underlying the association of cGAS-STING activity with various autoinflammatory, autoimmune and degenerative diseases. Finally, we outline the chemical nature of recently developed cGAS and STING antagonists and summarize their potential clinical applications.
© 2021. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
A.A. is a member of the scientific advisory board of IFM Therapeutics and scientific co-founder of IFM Due. J.D.K. and S.V. are employees of IFM Therapeutics. A.D. declares no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

