The Mechanism of Penehyclidine Hydrochloride and Its Effect on the Inflammatory Response of Lung Tissue in Rats with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease During Mechanical Ventilation
- PMID: 33833508
- PMCID: PMC8020330
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S295329
The Mechanism of Penehyclidine Hydrochloride and Its Effect on the Inflammatory Response of Lung Tissue in Rats with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease During Mechanical Ventilation
Retraction in
-
The Mechanism of Penehyclidine Hydrochloride and Its Effect on the Inflammatory Response of Lung Tissue in Rats with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease During Mechanical Ventilation [Retraction].Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2023 May 26;18:1003-1004. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S422900. eCollection 2023. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2023. PMID: 37265941 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Penehyclidine hydrochloride is a selective antagonist of M1 and M3 receptors. Clinical studies suggest that it is a potential drug for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of penehyclidine hydrochloride on the inflammatory response of lung tissue during mechanical ventilation in rats with COPD and explore the role of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase/stress-activated protein kinase (JNK/SAPK) signaling pathway.
Methods: Eight-week-old male Sprague Dawley rats were exposed to cigarette smoke for 30 minutes every day for two months, and on the first and thirtieth days, 200 ug of lipopolysaccharide was injected into the trachea. Two months later, the rats were randomly divided into the control group (C), model group (M), model + normal saline group (N), and penehyclidine hydrochloride group (H) to undergo anesthesia and mechanical ventilation. In group H, 1 mg/kg of penehyclidine hydrochloride was injected intravenously.
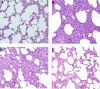
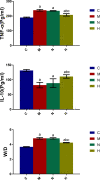
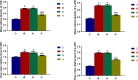
Results: The results showed that: ① Compared with group C, the other groups all showed typical chronic obstructive pathological changes in the lung tissue; their wet/dry weight ratio (W/D), TNF-α, JNK, and p-JNK levels increased (P < 0.05), and their interleukin (IL)-10 levels decreased (P < 0.05). ② Compared with group M, there was no significant change in the lung tissue indexes in group N (P > 0.05). ③ Compared with group N, the W/D, TNF-α, JNK, and p-JNK levels in group H decreased (P < 0.05), while the levels of IL-10 increased (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Penehyclidine hydrochloride can alleviate the pulmonary inflammatory response in rats with COPD undergoing mechanical ventilation. The JNK/SAPK signaling pathway may be involved in this process.
Keywords: IL-10; JNK; TNF-α; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; p-JNK; penehyclidine hydrochloride.
© 2021 Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
-
- Chen ZY, Wu JH, Fu YY, et al. Analysis of respiratory mechanisms in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients under the effects of penehyclidine hydrochloride combined with continuous positive airway pressure ventilation. J Med Imaging Health Inf. 2020;10(10):1395–1400. doi: 10.1166/jmihi.2020.3055 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

