Stability Determination of an Extemporaneously Compounded Ambrisentan Suspension by High Performance Liquid Chromatography Analysis
- PMID: 33833628
- PMCID: PMC8021248
- DOI: 10.5863/1551-6776-26.3.265
Stability Determination of an Extemporaneously Compounded Ambrisentan Suspension by High Performance Liquid Chromatography Analysis
Abstract
Objective: Ambrisentan, an endothelin receptor antagonist FDA-approved for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension in adult patients, lacks an acceptable pediatric dosage form. The objective of this investigation was to determine the stability of an extemporaneously compounded ambrisentan suspension.
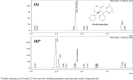
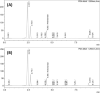
Methods: Ambrisentan suspension was compounded to a concentration of 1 mg/mL using commercially available suspending agents. The suspension was then evenly split into 2 plastic amber prescription bottles. One bottle was stored at room temperature and under continuous fluorescent light while the other bottle was stored under refrigeration and protection from light. A fast and selective reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method was developed and validated for the analysis of ambrisentan. HPLC analysis was performed on samples withdrawn from the stock bottles at predetermined time intervals, up to 90 days.
Results: The developed HPLC method enabled the elution and detection of ambrisentan peak at 4.4 minutes. HPLC analysis revealed that all samples from both storage conditions retained >90% potency throughout the study timeframe. There were no signs of any ambrisentan breakdown products on HPLC analysis. Color and odor of the final product was also consistent throughout the 90-day storage period.
Conclusion: Ambrisentan suspension, compounded to 1 mg/mL, is stable at room temperature or under refrigeration for up to 90 days.
Keywords: ambrisentan; chromatography, high performance liquid; drug compounding; drug stability; pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Copyright. Pediatric Pharmacy Association. All rights reserved. For permissions, email: mhelms@pediatricpharmacy.org 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure. The authors declare no conflicts or financial interest in any product or service mentioned in the manuscript, including grants, equipment, medications, employment, gifts, and honoraria. The authors had full access to all data and take responsibility for the integrity and accuracy of the data analysis.
Figures

References
-
- Ivy DD, Abman SH, Barst RJ et al. Pediatric pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62(suppl 25):D117–D126. - PubMed
-
- Barst RJ, Ivy DD, Foreman AJ et al. Four- and seven-year outcomes of patients with congenital heart disease-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension (from the REVEAL Registry) Am J Cardiol. 2014;113(1):147–155. - PubMed
-
- Galiè N, Olschewski H, Oudiz RJ et al. Ambrisentan for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension: results of the ambrisentan in pulmonary arterial hyper-tension, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter, efficacy (ARIES) study 1 and 2. Am J Cardiol. 2014;113(1):147–155. - PubMed
-
- Oudiz RJ, Galiè N, Olschewski H et al. Long-term ambrisentan therapy for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54(21):1971–1981. - PubMed
-
- Galie N, Barbera JA, Frost AE et al. Initial use of ambrisentan plus tadalafil in pulmonary arterial hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(9):834–844. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
