Why Ablation of Sites With Purkinje Activation Is Antiarrhythmic: The Interplay Between Fast Activation and Arrhythmogenesis
- PMID: 33833689
- PMCID: PMC8021688
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2021.648396
Why Ablation of Sites With Purkinje Activation Is Antiarrhythmic: The Interplay Between Fast Activation and Arrhythmogenesis
Abstract
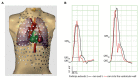
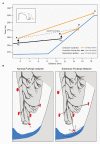
Ablation of sites showing Purkinje activity is antiarrhythmic in some patients with idiopathic ventricular fibrillation (iVF). The mechanism for the therapeutic success of ablation is not fully understood. We propose that deeper penetrance of the Purkinje network allows faster activation of the ventricles and is proarrhythmic in the presence of steep repolarization gradients. Reduction of Purkinje penetrance, or its indirect reducing effect on apparent propagation velocity may be a therapeutic target in patients with iVF.
Keywords: Purkinje; ablation; arrhythmias; early repolarization syndrome; electrophysiology; idiopathic ventricular fibrillation.
Copyright © 2021 Coronel, Potse, Haïssaguerre, Derval, Rivaud, Meijborg, Cluitmans, Hocini and Boukens.
Conflict of interest statement
MC is part-time employed by Philips Research. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Allison J. S., Qin H., Dosdall D. J., Huang J., Newton J. C., Allred J. D., et al. (2007). The transmural activation sequence in porcine and canine left ventricle is markedly different during long-duration ventricular fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 18, 1306–1312. 10.1111/j.1540-8167.2007.00963.x, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

