Dietary Lipid Modulation of Intestinal Serotonin in Ballan Wrasse (Labrus bergylta)- In Vitro Analyses
- PMID: 33833735
- PMCID: PMC8021958
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2021.560055
Dietary Lipid Modulation of Intestinal Serotonin in Ballan Wrasse (Labrus bergylta)- In Vitro Analyses
Abstract
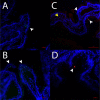
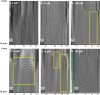
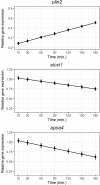
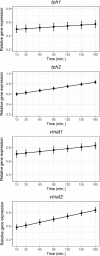
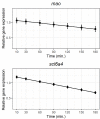
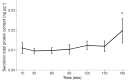
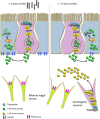
Serotonin (5-HT) is pivotal in the complex regulation of gut motility and consequent digestion of nutrients via multiple receptors. We investigated the serotonergic system in an agastric fish species, the ballan wrasse (Labrus bergylta) as it represents a unique model for intestinal function. Here we present evidence of the presence of enterochromaffin cells (EC cells) in the gut of ballan wrasse comprising transcriptomic data on EC markers like adra2a, trpa1, adgrg4, lmxa1, spack1, serpina10, as well as the localization of 5-HT and mRNA of the rate limiting enzyme; tryptophan hydroxylase (tph1) in the gut epithelium. Second, we examined the effects of dietary marine lipids on the enteric serotonergic system in this stomach-less teleost by administrating a hydrolyzed lipid bolus in ex vivo guts in an organ bath system. Modulation of the mRNA expression from the tryptophan hydroxylase tph1 (EC cells isoform), tph2 (neural isoform), and other genes involved in the serotonergic machinery were tracked. Our results showed no evidence to confirm that the dietary lipid meal did boost the production of 5-HT within the EC cells as mRNA tph1 was weakly regulated postprandially. However, dietary lipid seemed to upregulate the post-prandial expression of tph2 found in the serotonergic neurons. 5-HT in the intestinal tissue increased 3 hours after "exposure" of lipids, as was observed in the mRNA expression of tph2. This suggest that serotonergic neurons and not EC cells are responsible for the substantial increment of 5-HT after a lipid-reach "meal" in ballan wrasse. Cells expressing tph1 were identified in the gut epithelium, characteristic for EC cells. However, Tph1 positive cells were also present in the lamina propria. Characterization of these cells together with their implications in the serotonergic system will contribute to broad the scarce knowledge of the serotonergic system across teleosts.
Keywords: EC-cell; gut motility; in vitro; lipids; teleost.
Copyright © 2021 Etayo, Le, Araujo, Lie and Sæle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Loss of stomach, loss of appetite? Sequencing of the ballan wrasse (Labrus bergylta) genome and intestinal transcriptomic profiling illuminate the evolution of loss of stomach function in fish.BMC Genomics. 2018 Mar 6;19(1):186. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4570-8. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29510660 Free PMC article.
-
Essential roles of enteric neuronal serotonin in gastrointestinal motility and the development/survival of enteric dopaminergic neurons.J Neurosci. 2011 Jun 15;31(24):8998-9009. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6684-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21677183 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Cholecystokinin (CCK) on Gut Motility in the Stomachless Fish Ballan Wrasse (Labrus bergylta).Front Neurosci. 2019 Jun 7;13:553. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00553. eCollection 2019. Front Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31231179 Free PMC article.
-
The ever-changing roles of serotonin.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2020 Aug;125:105776. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2020.105776. Epub 2020 May 29. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32479926 Review.
-
The Diverse Metabolic Roles of Peripheral Serotonin.Endocrinology. 2017 May 1;158(5):1049-1063. doi: 10.1210/en.2016-1839. Endocrinology. 2017. PMID: 28323941 Review.
References
-
- Jackson D, Cotter D, Newell J, McEvoy S, O’Donohoe P, Kane F, et al. . Impact of Lepeophtheirus salmonis infestations on migrating Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L., smolts at eight locations in Ireland with an analysis of lice-induced marine mortality. J Fish Dis (2013) 36(3):273–81. 10.1111/jfd.12054 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lie KK, Tørresen OK, Solbakken MH, Rønnestad I, Tooming-Klunderud A, Nederbragt AJ, et al. . Loss of stomach, loss of appetite? Sequencing of the ballan wrasse (Labrus bergylta) genome and intestinal transcriptomic profiling illuminate the evolution of loss of stomach function in fish. BMC Genomics (2018) 19(1):186. 10.1186/s12864-018-4570-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Le HTMD, Shao X, Krogdahl Å, Kortner TM, Lein I, Kousoulaki K, et al. . Intestinal function of the stomachless fish, ballan wrasse (Labrus bergylta). Front Marine Sci (2019) 6(140):1–15. 10.3389/fmars.2019.00140 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

