The Role of Unfolded Protein Response in Human Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: Perk and IRE1- α as Two Potential Therapeutic Targets
- PMID: 33833850
- PMCID: PMC8016586
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6492879
The Role of Unfolded Protein Response in Human Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: Perk and IRE1- α as Two Potential Therapeutic Targets
Abstract
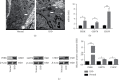
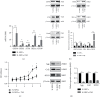
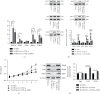
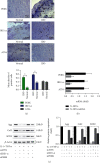
Inflammation plays a key role in intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD). The association between inflammation and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress has been observed in many diseases. However, whether ER stress plays an important role in IDD remains unclear. Therefore, this study is aimed at investigating the expression of ER stress in IDD and at exploring the underlying mechanisms of IDD, ER stress, and inflammation. The expression of ER stress was activated in nucleus pulposus cells from patients who had IDD (D-NPCs) compared with patients without IDD (N-NPCs); and both the proliferation and synthesis capacity were decreased by inducer tunicamycin (Tm) and proinflammatory cytokines. Pretreatment of NPCs with 4-phenyl butyric acid (4-PBA) prevented the inflammatory cytokine-induced upregulation of unfolded protein response- (UPR-) related proteins and recovered cell synthetic ability. Furthermore, proinflammatory cytokine treatment significantly upregulated the expression of inositol-requiring protein 1 (IRE1-α) and protein kinase RNA-like ER kinase (PERK), but not activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6). Finally, knockdown of IRE1-α and PERK also restored the biological activity of NPCs. Our findings identified that IRE1-α and PERK might be the potential targets for IDD treatment, which may help illustrate the underlying mechanism of ER stress in IDD.
Copyright © 2021 Tianyong Wen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of IRE1 suppresses the catabolic effect of IL-1β on nucleus pulposus cell and prevents intervertebral disc degeneration in vivo.Biochem Pharmacol. 2022 Mar;197:114932. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.114932. Epub 2022 Jan 24. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35085541
-
Protein kinase RNA-like ER kinase/eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2α pathway attenuates tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced apoptosis in nucleus pulposus cells by activating autophagy.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Jul;234(7):11631-11645. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27820. Epub 2018 Dec 4. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30515797
-
The kinase PERK and the transcription factor ATF4 play distinct and essential roles in autophagy resulting from tunicamycin-induced ER stress.J Biol Chem. 2019 May 17;294(20):8197-8217. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002829. Epub 2019 Mar 29. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30926605 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular signal networks and regulating mechanisms of the unfolded protein response.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2017 Jan.;18(1):1-14. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1600043. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2017. PMID: 28070992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Basis of Human Diseases and Targeted Therapy Based on Small-Molecule Inhibitors of ER Stress-Induced Signaling Pathways.Curr Mol Med. 2017;17(2):118-132. doi: 10.2174/1566524017666170306122643. Curr Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28266275 Review.
Cited by
-
Panax notoginseng saponin reduces IL-1β-stimulated apoptosis and endoplasmic reticulum stress of nucleus pulposus cells by suppressing miR-222-3p.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Jul;10(13):748. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-3203. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35957710 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum-Dependent Apoptotic Response to Cellular Stress in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 11;26(6):2489. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062489. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141133 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the underlying pathogenesis and therapeutic potential of endoplasmic reticulum stress in degenerative musculoskeletal diseases.Mil Med Res. 2023 Nov 9;10(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s40779-023-00485-5. Mil Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37941072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive analysis of senescence-related genes and immune infiltration in intervertebral disc degeneration: a meta-data approach utilizing bulk and single-cell RNA sequencing data.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Dec 22;10:1296782. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1296782. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 38187091 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress: An Emerging Therapeutic Target for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Feb 1;9:819139. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.819139. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35178406 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

