Early Experience with Biobranetm for Definitive Coverage of Tangentially Excised Partial-Thickness Thermal Burns
- PMID: 33833964
- PMCID: PMC8016370
- DOI: 10.29252/wjps.10.1.119
Early Experience with Biobranetm for Definitive Coverage of Tangentially Excised Partial-Thickness Thermal Burns
Abstract
BiobraneTM is a popular biosynthetic semi-permeable skin substitute conventionally applied onto non-excised partial thickness burn wounds to facilitate healing. The use of BiobraneTM for definitive coverage after excision of partial-thickness thermal burns has not been reported. We highlighted our experience of immediate BiobraneTM application for definitive coverage of tangentially-excised partial thickness thermal burn wounds in four patients. This technique is safe and efficient, minimizes painful and costly dressing changes, avoids the complications associated with autologous skin grafting, and eliminates the unpredictability of burns wound conversion. We believe this method expands the indications for BiobraneTM usage, accelerates wound healing, and provides better aesthetic outcomes.
Keywords: Biobrane; Burns excision; Partial-thickness burns; Skin substitute; Wound healing.
Figures
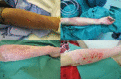
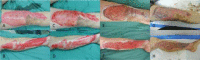
References
-
- Ong YS, Samuel M, Song C. Meta-analysis of early excision of burns. Burns. 2006;32:145–50. - PubMed
-
- Smith DJ Jr. Use of Biobrane in wound management. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1995;16:317–20. - PubMed
-
- Whitaker IS, Worthington S, Jivan S, Phipps A. The use of Biobrane by burn units in the United Kingdom: a national study. Burns. 2007;33:1015–20. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
