Using lncRNA Sequencing to Reveal a Putative lncRNA-mRNA Correlation Network and the Potential Role of PCBP1-AS1 in the Pathogenesis of Cervical Cancer
- PMID: 33833992
- PMCID: PMC8023048
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.634732
Using lncRNA Sequencing to Reveal a Putative lncRNA-mRNA Correlation Network and the Potential Role of PCBP1-AS1 in the Pathogenesis of Cervical Cancer
Abstract
Background/aims: Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) play important roles in many diseases and participate in posttranscriptional regulatory networks in tumors. However, the functions of major lncRNAs in cervical cancer are unclear. Therefore, the aim of this study was to construct a lncRNA-mRNA coexpression functional network and analyze lncRNAs that might contribute to the pathogenesis of cervical cancer.
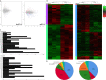
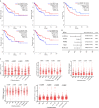
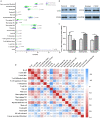
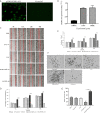
Methods: Differentially expressed lncRNAs (DElncRNAs) and mRNAs (DEmRNAs) between three pairs of cervical cancer tissues and adjacent mucosa were identified by lncRNA microarray analysis. LncRNA-mRNA correlation analysis and functional enrichment were performed on the DEGs. From the correlation network, PCBP1-AS1 was selected as a candidate for further analysis. PCBP1-AS1 expression was examined by qPCR, and Kaplan-Meier survival, clinicopathology, GSEA, and immune infiltration analysis of PCBP1-AS1 were performed. The immune responses of PCBP1-AS1 expression in cervical cancer were analyzed using TIMER and western blot. PCBP1-AS1 was knocked down and overexpressed to evaluate its role in cell proliferation, migration, and invasion.
Results: A total of 130 lncRNAs were significantly differentially expressed in cervical cancer patient samples compared with control samples. Differentially expressed mRNAs in the lncRNA-mRNA interaction network were involved in the EMT process. Combined with the Kaplan-Meier survival analyses, the coexpression network revealed that PCBP1-AS1 was significantly associated with OS and clinicopathological parameters in cervical cancer patients. Moreover, PCBP1-AS1 expression was not only significantly increased in cervical cancer specimens but also associated with tumor stage, TNM, and invasion. GSEA revealed that PCBP1-AS1 is closely correlated with cell biological function via the p53 and notch signaling pathways. TIMER analysis revealed that the numbers of NK cells and M2 macrophages decreased when PCBP1-AS1 expression was high, which was consistent with the western blot results in clinical samples. Furthermore, in vitro experiments showed that high expression of PCBP1-AS1 promoted cell proliferation, migration, and invasion.
Conclusions: Transcriptomic and lncRNA-mRNA correlation analyses revealed that PCBP1-AS1 plays a key role as an independent prognostic factor in patients with cervical cancer. The identification of PCBP1-AS1 as a new biomarker for cervical cancer could help explain how changes in the immune environment promote cervical cancer development.
Keywords: cervical cancer; lncRNA sequencing; lncRNA-mRNA correlation network; long non-coding RNA; proliferation.
Copyright © 2021 Li, Peng, Gong, Ling, Xu and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

