PCSK9 Functions in Atherosclerosis Are Not Limited to Plasmatic LDL-Cholesterol Regulation
- PMID: 33834043
- PMCID: PMC8021767
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.639727
PCSK9 Functions in Atherosclerosis Are Not Limited to Plasmatic LDL-Cholesterol Regulation
Abstract
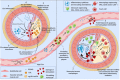
The relevance of PCSK9 in atherosclerosis progression is demonstrated by the benefits observed in patients that have followed PCSK9-targeted therapies. The impact of these therapies is attributed to the plasma lipid-lowering effect induced when LDLR hepatic expression levels are recovered after the suppression of soluble PCSK9. Different studies show that PCSK9 is involved in other mechanisms that take place at different stages during atherosclerosis development. Indeed, PCSK9 regulates the expression of key receptors expressed in macrophages that contribute to lipid-loading, foam cell formation and atherosclerotic plaque formation. PCSK9 is also a regulator of vascular inflammation and its expression correlates with pro-inflammatory cytokines release, inflammatory cell recruitment and plaque destabilization. Furthermore, anti-PCSK9 approaches have demonstrated that by inhibiting PCSK9 activity, the progression of atherosclerotic disease is diminished. PCSK9 also modulates thrombosis by modifying platelets steady-state, leukocyte recruitment and clot formation. In this review we evaluate recent findings on PCSK9 functions in cardiovascular diseases beyond LDL-cholesterol plasma levels regulation.
Keywords: LDL—cholesterol; PCSK9 (proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin type 9); atherosclerosis; inflammation; lipid loading; lipoprotein receptors.
Copyright © 2021 Luquero, Badimon and Borrell-Pages.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Zhang DW, Lagace TA, Garuti R, Zhao Z, McDonald M, Horton JD, et al. Binding of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 to epidermal growth factor-like repeat A of low density lipoprotein receptor decreases receptor recycling and increases degradation. J Biol Chem. (2007) 282:18602–12. 10.1074/jbc.M702027200 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Seidah NG, Benjannet S, Wickham L, Marcinkiewicz J, Bélanger Jasmin S, Stifani S, et al. The secretory proprotein convertase neural apoptosis-regulated convertase 1 (NARC-1): liver regeneration and neuronal differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2003) 100:928–33. 10.1073/pnas.0335507100 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous