Advanced feature selection to study the internationalization strategy of enterprises
- PMID: 33834097
- PMCID: PMC8022633
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj-cs.403
Advanced feature selection to study the internationalization strategy of enterprises
Abstract
Firms face an increasingly complex economic and financial environment in which the access to international networks and markets is crucial. To be successful, companies need to understand the role of internationalization determinants such as bilateral psychic distance, experience, etc. Cutting-edge feature selection methods are applied in the present paper and compared to previous results to gain deep knowledge about strategies for Foreign Direct Investment. More precisely, evolutionary feature selection, addressed from the wrapper approach, is applied with two different classifiers as the fitness function: Bagged Trees and Extreme Learning Machines. The proposed intelligent system is validated when applied to real-life data from Spanish Multinational Enterprises (MNEs). These data were extracted from databases belonging to the Spanish Ministry of Industry, Tourism, and Trade. As a result, interesting conclusions are derived about the key features driving to the internationalization of the companies under study. This is the first time that such outcomes are obtained by an intelligent system on internationalization data.
Keywords: Bagged decision trees; Evolutionary feature selection; Extreme learning machines; Internationaliza-tion; Multinational enterprises.
© 2021 Herrero et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
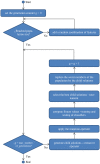
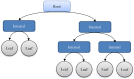
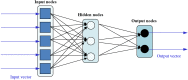
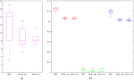
References
-
- Ambos B, Leicht-Deobald U, Leinemann A. Understanding the formation of psychic distance perceptions: are country-level or individual-level factors more important? International Business Review. 2019;28(4):660–671. doi: 10.1016/j.ibusrev.2019.01.003. - DOI
-
- Argote L, Beckman SL, Epple D. The persistence and transfer of learning in industrial settings. Management Science. 1990;36(2):140–154. doi: 10.1287/mnsc.36.2.140. - DOI
-
- Azar G, Drogendijk R. Psychic distance, innovation, and firm performance. Management International Review. 2014;54(5):581–613. doi: 10.1007/s11575-014-0219-2. - DOI
-
- Barnard C, Simon HA. Administrative behavior: a study of decision-making processes in administrative organization. New York: Free Press; 1947.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
