An update on the prevalence of eating disorders in the general population: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 33834377
- PMCID: PMC8933366
- DOI: 10.1007/s40519-021-01162-z
An update on the prevalence of eating disorders in the general population: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: To update the prevalence of eating disorders in the general population before 2021 and to analyze the distribution characteristics at different times and in different regions and sexes, as well as the diagnostic criteria.
Methods: Based on the method from a previous report by the authors, studies were identified from the following databases: PubMed/Medline, PsycINFO, ISI Web of Knowledge, Ovid and the 4 most important Chinese databases. Articles in English and Chinese before 2021 were retrieved. The data retrieved at this time were pooled with the data from a previous report for analyses.
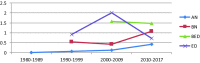
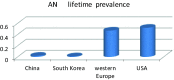
Results: Thirty-three studies were identified, which included 18 studies supplemented in this retrieval. The pooled lifetime and 12-month prevalence of eating disorders were 0.91% (95% CI, 0.48-1.71) and 0.43% (95% CI, 0.18-0.78), respectively. The pooled lifetime and 12-month prevalence of the subgroup EDs (any), which covers all types of eating disorders, were 1.69% and 0.72%, respectively. The lifetime prevalence of AN, BN and BED was 0.16% (95% CI, 0.06-0.31), 0.63% (95% CI, 0.33-1.02) and 1.53% (95% CI, 1.00-2.17), respectively. The lifetime prevalence of EDs in Western countries was 1.89%, and was high at 2.58% in females. Prevalence studies using DSM-5 criteria were scarce.
Conclusions: The prevalence of eating disorders might be underestimated thus far. Not all types of EDs were included in a majority of epidemiological surveys, and the prevalence rates of the new types of EDs were significantly higher. Eating disorders were especially common in Western countries and in females. New diagnostic criteria should be used to comprehensively assess all types of eating disorders.
Level of evidence: 1, systematic review and meta-analysis.
Keywords: Anorexia nervosa (AN); Binge eating disorder (BED); Bulimia nervosa (BN); Eating disorders (EDs); General population; Prevalence.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interest related to this article.
Figures


References
-
- Hay P, Mitchison D, Collado AEL, González-Chica DA, Stocks N, Touyz S. Burden and health-related quality of life of eating disorders, including Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder (ARFID), in the Australian population. J Eat Disord. 2017;5(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s40337-017-0149-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Keski-Rahkonen A, Mustelin L. Epidemiology of eating disorders in Europe: prevalence, incidence, comorbidity, course, consequences, and risk factors. CurrOpin Psychiatry. 2016;29(6):340–345. - PubMed
-
- 陈珏. 进食障碍诊疗新进展及其对全科医生的启示. 中国全科医学. (2019)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

