[Sitagliptin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in human gingival fibroblasts by blocking nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway]
- PMID: 33834669
- PMCID: PMC8055776
- DOI: 10.7518/hxkq.2021.02.005
[Sitagliptin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in human gingival fibroblasts by blocking nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway]
Abstract
Objectives: This study was performed to clarify the effects of sitagliptin on Porphyromonas gingivalis-lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory response in human gingival fibroblasts (HGFs), explore the molecular mechanism of its roles, and provide a foundation for clinical therapeutics in periodontitis.
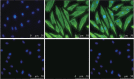
Methods: Healthy gingival samples were collected from the donors. HGFs were isolated with enzymic digestion method and identified. The effects of LPS and sitagliptin on cell viability were detected by cell-counting kit-8 (CCK8). The mRNA levels of inflammatory cytokines, namely, interleukin (IL)-6, IL-8, C-C motif ligand 2 (CCL2), and superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2), were evaluated by quantity real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and enzyme-linked immune sorbent assay (ELISA) was used to measure the secretion protein levels of IL-6, IL-8, and CCL2. Western blot analysis was used to further investigate the activation of nuclear factor (NF)-κB signaling pathway. The effect of NF-κB pathway inhibitor BAY11-7082 on LPS-induced HGF inflammatory cytokines at the gene level was verified by qRT-PCR.
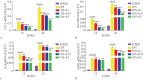
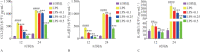
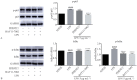
Results: Low concentrations of sitagliptin (0.1, 0.25, and 0.5 µmol·L-1) did not affect HGF growth in 24 and 48 h, whereas high concentrations of sitagliptin (5-1 000 µmol·L-1) significantly inhibited cell proliferation. Sitagliptin suppressed 5 µg·mL-1 of LPS-induced IL-6, IL-8, CCL2, and SOD2 gene expression levels in HGF in a concentration-dependent manner. Furthermore, sitagliptin significantly decreased the elevated secretion of IL-6, IL-8, and CCL2 protein induced by LPS. Western blot analysis showed that 0.5 µmol·L-1 of sitagliptin significantly inhibited LPS-induced NF-κB signaling pathway activation. Results of qRT-PCR analysis indicated that 0.5 µmol·L-1 of sitagliptin and 5 µmol·L-1 of BAY11-7082 significantly inhibited LPS-induced IL-6, IL-8, CCL2, and SOD2 gene expressions.
Conclusions: Sitagliptin could significantly inhibit LPS-induced HGF inflammatory response by blocking the NF-κB signaling pathway activation.
目的: 明确西格列汀对牙龈卟啉单胞菌脂多糖(LPS)诱导的人牙龈成纤维细胞(HGF)炎症反应的影响,并探讨其发挥作用的分子学机制,为未来西格列汀在牙周炎治疗中的应用提供初步的实验依据。方法: 收集临床患者健康牙龈组织标本,利用酶消化法分离培养HGF并进行细胞来源鉴定;采用细胞增殖-毒性检测试剂盒检测LPS和西格列汀与HGF共培养24、48 h细胞增殖变化;通过实时荧光定量聚合酶链式反应(qRT-PCR)检测炎性细胞因子白细胞介素(IL)-6、IL-8、趋化因子配体2(CCL2)、超氧化物歧化酶2(SOD2)的基因表达水平;酶联免疫吸附实验检测细胞培养上清液中IL-6、IL-8和CCL2的蛋白表达水平;应用蛋白免疫印迹法检测核因子-κB(NF-κB)信号通路的激活情况,通过qRT-PCR验证NF-κB通路抑制剂BAY11-7082对LPS诱导的HGF炎症细胞因子基因表达水平的影响。结果: 低浓度的西格列汀(0.1、0.25、0.5 µmol·L-1)作用24、48 h对HGF的生长无影响,而高浓度西格列汀(5~1 000 µmol·L-1)明显抑制了细胞增殖。西格列汀浓度依赖性抑制5 µg·mL-1 LPS诱导的HGF中IL-6、IL-8、CCL2和SOD2的基因表达水平。此外,西格列汀显著抑制LPS诱导的IL-6、IL-8和CCL2蛋白表达水平。蛋白免疫印迹结果表明:0.5 µmol·L-1西格列汀显著性抑制了LPS诱导的NF-κB信号通路激活,qRT-PCR结果表明0.5 µmol·L-1西格列汀与5 µmol·L-1BAY11-7082均显著抑制了LPS诱导的IL-6、IL-8、CCL2和SOD2的基因表达水平。结论: 西格列汀通过阻断NF-κB信号通路的激活来抑制LPS诱导的HGF炎症反应。.
Keywords: Sitagliptin; human gingival fibroblasts; inflammation; lipopolysaccharide; nuclear factor-κB.
Conflict of interest statement
利益冲突声明:作者声明本文无利益冲突。
Figures


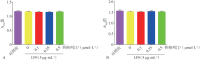

Similar articles
-
Quercetin Inhibits Inflammatory Response Induced by LPS from Porphyromonas gingivalis in Human Gingival Fibroblasts via Suppressing NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Aug 20;2019:6282635. doi: 10.1155/2019/6282635. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31531360 Free PMC article.
-
Rho-kinase inhibitor Y-27632 downregulates LPS-induced IL-6 and IL-8 production via blocking p38 MAPK and NF-κB pathways in human gingival fibroblasts.J Periodontol. 2018 Jul;89(7):883-893. doi: 10.1002/JPER.17-0571. J Periodontol. 2018. PMID: 29630729
-
[Inhibitory effect of downregulating G protein-coupled receptor class C group 5 member A expression on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in human gingival fibroblasts].Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Apr 9;59(4):344-353. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112144-20231107-00241. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38548591 Chinese.
-
Biological effects of interleukin-6 on Gingival Fibroblasts: Cytokine regulation in periodontitis.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Sep;233(9):6393-6400. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26521. Epub 2018 Mar 25. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29574949 Review.
-
Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide signaling in gingival fibroblasts-CD14 and Toll-like receptors.Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2002;13(2):132-42. doi: 10.1177/154411130201300204. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2002. PMID: 12097356 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of sitagliptin activation of the stromal cell-derived factor-1/CXC chemokine receptor 4 signaling pathway on the proliferation, apoptosis, inflammation, and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells induced by lipopolysaccharide.Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Feb 1;42(1):37-45. doi: 10.7518/hxkq.2024.2023213. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38475949 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
References
-
- Ji S, Choi YS, Choi Y. Bacterial invasion and persistence: critical events in the pathogenesis of periodontitis[J] J Periodontal Res. 2015;50(5):570–585. - PubMed
-
- Chapple IL, Matthews JB. The role of reactive oxygen and antioxidant species in periodontal tissue destruction[J] Periodontol 2000. 2007;43:160–232. - PubMed
-
- Meyle J, Chapple I. Molecular aspects of the pathogenesis of periodontitis[J] Periodontol 2000. 2015;69(1):7–17. - PubMed
-
- Laine ML, Crielaard W, Loos BG. Genetic susceptibility to periodontitis[J] Periodontol 2000. 2012;58(1):37–68. - PubMed
-
- Bostanci N, Belibasakis GN. Porphyromonas gingivalis: an invasive and evasive opportunistic oral pathogen[J] FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2012;333(1):1–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
