Calculation of therapeutic antibody viscosity with coarse-grained models, hydrodynamic calculations and machine learning-based parameters
- PMID: 33834944
- PMCID: PMC8043186
- DOI: 10.1080/19420862.2021.1907882
Calculation of therapeutic antibody viscosity with coarse-grained models, hydrodynamic calculations and machine learning-based parameters
Abstract
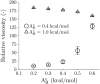
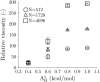
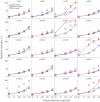
High viscosity presents a challenge for manufacturing and drug delivery of therapeutic antibodies. The viscosity is determined by protein-protein interactions among many antibodies. Molecular simulation is a promising method to study protein-protein interactions; however, all-atom models do not allow the simulation of multiple molecules, which is necessary to compute viscosity directly. Coarse-grained models, on the other hand can do this. In this work, a 12-bead coarse-grained model based on Swan and coworkers (J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 2867-2880) was applied to study antibody interactions. Two adjustable parameters related to the short-range interactions on the variable and constant regions were determined by fitting experimental data of 20 IgG1 monoclonal antibodies at 150 mg/mL. The root-mean-square deviation improved from 1 to 0.68, and the correlation coefficient improved from 0.63 to 0.87 compared to that of a previous model that assumed the short-range interactions were the same for all the beads. Our model is also able to calculate the viscosity over a wide range of concentrations without additional parameters. A tabulated viscosity based on our model is provided to facilitate antibody screening in early-stage design.
Keywords: Antibody viscosity; coarse-grained models; hydrodynamic calculations; molecular dynamics simulations.
Figures



References
-
- Goswami S, Wang W, Arakawa T, Ohtake S.. Developments and challenges for mAb-based therapeutics. Antibodies. 2013;2(3):452–500. doi:10.3390/antib2030452. - DOI
-
- Zhang Z, Liu Y. Recent progresses of understanding the viscosity of concentrated protein solutions. Current Opinion in Chemical Engineering. 2017;16:48–55. doi:10.1016/j.coche.2017.04.001. - DOI
-
- Connolly BD, Petry C, Yadav S, Demeule B, Ciaccio N, Moore JMR, Shire SJ, Gokarn YR. Weak interactions govern the viscosity of concentrated antibody solutions: high-throughput analysis using the diffusion interaction parameter. Biophysical Journal. 2012;103(1):69–78. doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2012.04.047. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
