Influence of G protein-biased agonists of μ-opioid receptor on addiction-related behaviors
- PMID: 33835467
- PMCID: PMC8413226
- DOI: 10.1007/s43440-021-00251-1
Influence of G protein-biased agonists of μ-opioid receptor on addiction-related behaviors
Abstract
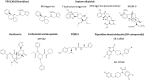
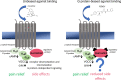
Opioid analgesics remain a gold standard for the treatment of moderate to severe pain. However, their clinical utility is seriously limited by a range of adverse effects. Among them, their high-addictive potential appears as very important, especially in the context of the opioid epidemic. Therefore, the development of safer opioid analgesics with low abuse potential appears as a challenging problem for opioid research. Among the last few decades, different approaches to the discovery of novel opioid drugs have been assessed. One of the most promising is the development of G protein-biased opioid agonists, which can activate only selected intracellular signaling pathways. To date, discoveries of several biased agonists acting via μ-opioid receptor were reported. According to the experimental data, such ligands may be devoid of at least some of the opioid side effects, such as respiratory depression or constipation. Nevertheless, most data regarding the addictive properties of biased μ-opioid receptor agonists are inconsistent. A global problem connected with opioid abuse also requires the search for effective pharmacotherapy for opioid addiction, which is another potential application of biased compounds. This review discusses the state-of-the-art on addictive properties of G protein-biased μ-opioid receptor agonists as well as we analyze whether these compounds can diminish any symptoms of opioid addiction. Finally, we provide a critical view on recent data connected with biased signaling and its implications to in vivo manifestations of addiction.
Keywords: Addiction; Dependence; G protein-biased opioids; Reward; Tolerance; Μ-opioid receptor.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Nothing to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biased Opioid Receptor Agonists: Balancing Analgesic Efficacy and Side-Effect Profiles.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 21;26(5):1862. doi: 10.3390/ijms26051862. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mu-Opioid receptor biased ligands: A safer and painless discovery of analgesics?Drug Discov Today. 2017 Nov;22(11):1719-1729. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2017.07.002. Epub 2017 Jul 22. Drug Discov Today. 2017. PMID: 28743488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Encoding mu-opioid receptor biased agonism with interaction fingerprints.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2021 Nov;35(11):1081-1093. doi: 10.1007/s10822-021-00422-5. Epub 2021 Oct 29. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2021. PMID: 34713377
-
Noribogaine is a G-protein biased κ-opioid receptor agonist.Neuropharmacology. 2015 Dec;99:675-88. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.08.032. Epub 2015 Aug 21. Neuropharmacology. 2015. PMID: 26302653
-
An updated assessment of the translational promise of G-protein-biased kappa opioid receptor agonists to treat pain and other indications without debilitating adverse effects.Pharmacol Res. 2022 Mar;177:106091. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106091. Epub 2022 Jan 29. Pharmacol Res. 2022. PMID: 35101565 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of pH on opioid receptor activation and implications for drug design.Biophys J. 2024 Dec 17;123(24):4158-4166. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2024.07.007. Epub 2024 Jul 5. Biophys J. 2024. PMID: 38970252 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vitro Analyses of Spinach-Derived Opioid Peptides, Rubiscolins: Receptor Selectivity and Intracellular Activities through G Protein- and β-Arrestin-Mediated Pathways.Molecules. 2021 Oct 8;26(19):6079. doi: 10.3390/molecules26196079. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34641621 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of an Addictive Potential of μ-Opioid Receptor Agonists with G Protein Bias: Behavioral and Molecular Modeling Studies.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Dec 27;14(1):55. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14010055. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 35056950 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Intracellular Signaling Activities of κ-Opioid Receptor Agonists, Nalfurafine Analogs; Focusing on the Selectivity of G-Protein- and β-Arrestin-Mediated Pathways.Molecules. 2022 Oct 19;27(20):7065. doi: 10.3390/molecules27207065. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36296658 Free PMC article.
-
Opioidergic Signaling-A Neglected, Yet Potentially Important Player in Atopic Dermatitis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 8;23(8):4140. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084140. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35456955 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Przewłocki R. Mechanisms of opioid analgesics addiction. Palliat Med Pract. 2017;11:55–60.
-
- Skolnick P. The opioid epidemic: crisis and solutions. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018;58:143–159. - PubMed
-
- Chan P, Lutfy K. Molecular changes in opioid addiction: the role of adenylyl cyclase and cAMP/PKA system. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2016;137:203–227. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
