Age-associated expression of p21and p53 during human wound healing
- PMID: 33835683
- PMCID: PMC8135007
- DOI: 10.1111/acel.13354
Age-associated expression of p21and p53 during human wound healing
Abstract
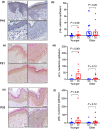
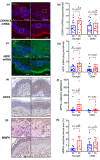
In mice, cellular senescence and senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) positively contribute to cutaneous wound healing. In this proof-of-concept study, we investigated the expressions of p16, p21, and other senescence-associated biomarkers during human wound healing in 24 healthy subjects using a double-biopsy experimental design. The first punch biopsy created the wound and established the baseline. The second biopsy, concentric to the first and taken several days after wounding, was used to probe for expression of biomarkers by immunohistochemistry and RNA FISH. To assess the effects of age, we recruited 12 sex-matched younger (30.2 ± 1.3 years) and 12 sex-matched older (75.6 ± 1.8 years) subjects. We found that p21 and p53, but not p16, were induced during healing in younger, but not older subjects. A role for Notch signaling in p21 expression was inferred from the inducible activation of HES1. Further, other SASP biomarkers such as dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4) were significantly induced upon wounding in both younger and older groups, whereas matrix metallopeptidase 9 (MMP9) was induced only in the younger group. Senescence-associated β-galactosidase (SA-β-gal) was not detectable before or after wounding. This pilot study suggests the possibility that human cutaneous wound healing is characterized by differential expression of p21 and p53 between younger and older subjects.
Keywords: aging; human wound healing; p21; p53.
© 2021 The Authors. Aging Cell published by the Anatomical Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
JC is a scientific founder of Unity Biotechnology. All other authors do not have any conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Basisty, N. , Kale, A. , Jeon, O. H. , Kuehnemann, C. , Payne, T. , Rao, C. , Holtz, A. , Shah, S. , Sharma, V. , Ferrucci, L. , Campisi, J. , & Schilling, B. (2020). A proteomic atlas of senescence‐associated secretomes for aging biomarker development. PLoS Biology, 18(1), e3000599. 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000599 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chigurupati, S. , Arumugam, T. V. , Son, T. G. , Lathia, J. D. , Jameel, S. , Mughal, M. R. , Tang, S.‐C. , Jo, D.‐G. , Camandola, S. , Giunta, M. , Rakova, I. , McDonnell, N. , Miele, L. , Mattson, M. P. , & Poosala, S. (2007). Involvement of notch signaling in wound healing. PLoS ONE, 2(11), e1167. 10.1371/journal.pone.0001167 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Demaria, M. , Ohtani, N. , Youssef, S. A. , Rodier, F. , Toussaint, W. , Mitchell, J. R. , Laberge, R.‐M. , Vijg, J. , Van Steeg, H. , Dollé, M. E. T. , Hoeijmakers, J. H. J. , de Bruin, A. , Hara, E. , & Campisi, J. (2014). An essential role for senescent cells in optimal wound healing through secretion of PDGF‐AA. Developmental Cell, 31(6), 722–733. 10.1016/j.devcel.2014.11.012 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

