Artificial Intelligence and Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer: 2020 Summative Review
- PMID: 33835956
- PMCID: PMC8041569
- DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000001762
Artificial Intelligence and Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer: 2020 Summative Review
Abstract
Despite considerable research efforts, pancreatic cancer is associated with a dire prognosis and a 5-year survival rate of only 10%. Early symptoms of the disease are mostly nonspecific. The premise of improved survival through early detection is that more individuals will benefit from potentially curative treatment. Artificial intelligence (AI) methodology has emerged as a successful tool for risk stratification and identification in general health care. In response to the maturity of AI, Kenner Family Research Fund conducted the 2020 AI and Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer Virtual Summit (www.pdac-virtualsummit.org) in conjunction with the American Pancreatic Association, with a focus on the potential of AI to advance early detection efforts in this disease. This comprehensive presummit article was prepared based on information provided by each of the interdisciplinary participants on one of the 5 following topics: Progress, Problems, and Prospects for Early Detection; AI and Machine Learning; AI and Pancreatic Cancer-Current Efforts; Collaborative Opportunities; and Moving Forward-Reflections from Government, Industry, and Advocacy. The outcome from the robust Summit conversations, to be presented in a future white paper, indicate that significant progress must be the result of strategic collaboration among investigators and institutions from multidisciplinary backgrounds, supported by committed funders.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. S.T.C., B. F., V.L.W.G., W.H., and D.S.K. are Kenner Family Research Fund scientific advisors. A.G., B.K., and L.R. are Kenner Family Research Fund board members.
Figures




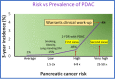



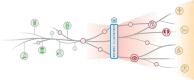

References
-
- Cancer Stat Facts: Pancreatic Cancer. Available at: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/pancreas.html. Accessed October 10, 2020.
-
- Canto M, Brentnall TA. Screening familial pancreatic cancer (FPC). Supplemental Digital Content 1. In: Chari ST, Kelly K, Hollingsworth MA, et al. Early detection of sporadic pancreatic cancer: summative review. Pancreas. 2015;44:693–712. Available at: http://links.lww.com/MPA/A372. Accessed August 14, 2020. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

