Uncertainties in synthetic DNA-based data storage
- PMID: 33836076
- PMCID: PMC8191772
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkab230
Uncertainties in synthetic DNA-based data storage
Abstract
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) has evolved to be a naturally selected, robust biomacromolecule for gene information storage, and biological evolution and various diseases can find their origin in uncertainties in DNA-related processes (e.g. replication and expression). Recently, synthetic DNA has emerged as a compelling molecular media for digital data storage, and it is superior to the conventional electronic memory devices in theoretical retention time, power consumption, storage density, and so forth. However, uncertainties in the in vitro DNA synthesis and sequencing, along with its conjugation chemistry and preservation conditions can lead to severe errors and data loss, which limit its practical application. To maintain data integrity, complicated error correction algorithms and substantial data redundancy are usually required, which can significantly limit the efficiency and scale-up of the technology. Herein, we summarize the general procedures of the state-of-the-art DNA-based digital data storage methods (e.g. write, read, and preservation), highlighting the uncertainties involved in each step as well as potential approaches to correct them. We also discuss challenges yet to overcome and research trends in the promising field of DNA-based data storage.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures



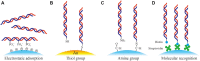
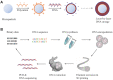
Similar articles
-
DNA-DISK: Automated end-to-end data storage via enzymatic single-nucleotide DNA synthesis and sequencing on digital microfluidics.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Aug 20;121(34):e2410164121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2410164121. Epub 2024 Aug 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39145927 Free PMC article.
-
Advances and Challenges in Random Access Techniques for In Vitro DNA Data Storage.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024 Aug 21;16(33):43102-43113. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c07235. Epub 2024 Aug 7. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 39110103 Review.
-
Low cost DNA data storage using photolithographic synthesis and advanced information reconstruction and error correction.Nat Commun. 2020 Oct 22;11(1):5345. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19148-3. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 33093494 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Micro-Disks for the Management of DNA-Based Data Storage with Index and Write-Once-Read-Many (WORM) Memory Features.Adv Mater. 2020 Sep;32(37):e2001249. doi: 10.1002/adma.202001249. Epub 2020 Jul 29. Adv Mater. 2020. PMID: 32725925
-
Carbon-based archiving: current progress and future prospects of DNA-based data storage.Gigascience. 2019 Jun 1;8(6):giz075. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giz075. Gigascience. 2019. PMID: 31220251 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Overcoming the High Error Rate of Composite DNA Letters-Based Digital Storage through Soft-Decision Decoding.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Aug;11(30):e2402951. doi: 10.1002/advs.202402951. Epub 2024 Jun 14. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38874370 Free PMC article.
-
Robust data storage in DNA by de Bruijn graph-based de novo strand assembly.Nat Commun. 2022 Sep 12;13(1):5361. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33046-w. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36097016 Free PMC article.
-
Controlled enzymatic synthesis of oligonucleotides.Commun Chem. 2024 Jun 18;7(1):138. doi: 10.1038/s42004-024-01216-0. Commun Chem. 2024. PMID: 38890393 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA Stability in Biodosimetry, Pharmacy and DNA Based Data-Storage: Optimal Storage and Handling Conditions.Chembiochem. 2022 Oct 19;23(20):e202200391. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202200391. Epub 2022 Sep 14. Chembiochem. 2022. PMID: 35972228 Free PMC article.
-
DNA-DISK: Automated end-to-end data storage via enzymatic single-nucleotide DNA synthesis and sequencing on digital microfluidics.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Aug 20;121(34):e2410164121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2410164121. Epub 2024 Aug 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39145927 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goda K., Kitsuregawa M.. The history of storage systems. Proc. IEEE. 2012; 100:1433–1440.
-
- Hilbert M., Lopez P.. The world's technological capacity to store, communicate, and compute information. Science. 2011; 332:60–65. - PubMed
-
- Reisel D., Gantz J., Rydning J.. Data age 2025: the digitization of the world from edge to core. Seagate. 2018; https://www.seagate.com/in/en/our-story/data-age-2025/.
-
- Xu Z.-W. Cloud-sea computing systems: Towards thousand-fold improvement in performance per watt for the coming zettabyte era. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2014; 29:177–181.
-
- Extance A. Could the molecule known for storing genetic information also store the world's data. Nature. 2016; 537:22–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

