FGF-MAPK signaling regulates human deep-layer corticogenesis
- PMID: 33836146
- PMCID: PMC8185433
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2021.03.014
FGF-MAPK signaling regulates human deep-layer corticogenesis
Abstract
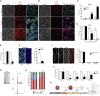
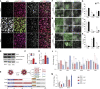
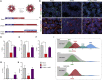
Despite heterogeneity across the six layers of the mammalian cortex, all excitatory neurons are generated from a single founder population of neuroepithelial stem cells. However, how these progenitors alter their layer competence over time remains unknown. Here, we used human embryonic stem cell-derived cortical progenitors to examine the role of fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and Notch signaling in influencing cell fate, assessing their impact on progenitor phenotype, cell-cycle kinetics, and layer specificity. Forced early cell-cycle exit, via Notch inhibition, caused rapid, near-exclusive generation of deep-layer VI neurons. In contrast, prolonged FGF2 promoted proliferation and maintained progenitor identity, delaying laminar progression via MAPK-dependent mechanisms. Inhibiting MAPK extended cell-cycle length and led to generation of layer-V CTIP2+ neurons by repressing alternative laminar fates. Taken together, FGF/MAPK regulates the proliferative/neurogenic balance in deep-layer corticogenesis and provides a resource for generating layer-specific neurons for studying development and disease.
Keywords: MAPK signaling; Notch; cortex; fibroblast growth factor 2; human neural development; lamination; neurogenesis; stem cells.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Betizeau M., Cortay V., Patti D., Pfister S., Gautier E., Bellemin-Menard A., Afanassieff M., Huissoud C., Douglas R.J., Kennedy H. Precursor diversity and complexity of lineage relationships in the outer subventricular zone of the primate. Neuron. 2013;80:442–457. - PubMed
-
- Bonnefont J., Tiberi L., van den Ameele J., Potier D., Gaber Z.B., Lin X., Bilheu A., Herpoel A., Velez Bravo F.D., Guillemot F. Cortical neurogenesis requires Bcl6-mediated transcriptional repression of multiple self-renewal-promoting extrinsic pathways. Neuron. 2019;103:1096–1108 e1094. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

