Performance of the RT-LAMP-based eazyplex® SARS-CoV-2 as a novel rapid diagnostic test
- PMID: 33836452
- PMCID: PMC8015392
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcv.2021.104817
Performance of the RT-LAMP-based eazyplex® SARS-CoV-2 as a novel rapid diagnostic test
Abstract
Background: Diagnostic assays for severe acute respiratory syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) that are easy to perform and produce fast results are essential for timely decision making regarding the isolation of contagious individuals.
Objective: We evaluated the CE-approved eazyplex® SARS-CoV-2, a ready-to-use real time RT-LAMP assay for identification of the SARS-CoV-2 N and ORF8 genes from swabs in less than 30 min without RNA extraction.
Study design: Oropharyngeal and nasal swabs from 100 positive and 50 negative patients were inoculated into 0.9 % saline and tested by NeuMoDx™ RT-PCR. An aliquot was diluted fivefold in Copan sputum liquefying (SL) solution and directly analyzed by eazyplex® SARS-CoV-2. In addition, 130 patient swabs were prospectively tested with both methods in parallel. Analytical sensitivity of the assay was determined using virus stock dilutions.
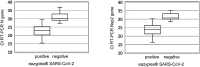
Results: Positive percent agreement (PPA) between the eazyplex® SARS-CoV-2 and RT-PCR was 74 % for samples with Ct values < 35. When using a Ct cut-off ≤ 28 the PPA increased to 97.4 %. In the prospective part of the study overall PPA of the eazyplex® kit was 66.7 % but increased to 100 % when only Ct values ≤ 28 were considered. There were no false positive results. The median time to positivity was 12.5 min for the N gene and 16.75 min for ORF8. Analytical sensitivity was 3.75 TCID50/mL. 105 virus copies/mL were reproducibly detected.
Conclusion: The eazyplex® SARS-CoV-2 is a rapid assay that accurately identifies samples with high viral loads. It may be useful for near-patient testing outside of a molecular diagnostic laboratory.
Keywords: POC; RT-LAMP; Rapid diagnostic test; SARS-CoV-2; Without RNA extraction.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Multiplex One-Step RT-qPCR Protocol to Detect SARS-CoV-2 in NP/OP Swabs and Saliva.Curr Protoc. 2021 May;1(5):e145. doi: 10.1002/cpz1.145. Curr Protoc. 2021. PMID: 34004070 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of a saliva molecular point of care for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 in ambulatory care.Sci Rep. 2021 Oct 26;11(1):21126. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-00560-8. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34702867 Free PMC article.
-
Adding saliva testing to oropharyngeal and deep nasal swab testing increases PCR detection of SARS-CoV-2 in primary care and children.Med J Aust. 2021 Sep 20;215(6):273-278. doi: 10.5694/mja2.51188. Epub 2021 Jul 20. Med J Aust. 2021. PMID: 34287935 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 by RT-PCR Using Different Sample Sources: Review of the Literature.Ear Nose Throat J. 2021 Apr;100(2_suppl):131S-138S. doi: 10.1177/0145561320953231. Epub 2020 Aug 31. Ear Nose Throat J. 2021. PMID: 32865458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detection profile of SARS-CoV-2 using RT-PCR in different types of clinical specimens: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Med Virol. 2021 Feb;93(2):719-725. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26349. Epub 2020 Aug 2. J Med Virol. 2021. PMID: 32706393 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
SARS-CoV-2 Testing of Emergency Department Patients Using cobas® Liat® and eazyplex® Rapid Molecular Assays.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jul 1;13(13):2245. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13132245. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37443639 Free PMC article.
-
Laboratory-based molecular test alternatives to RT-PCR for the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Oct 14;10(10):CD015618. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015618. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39400904
-
Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Detection of SARS-CoV-2 and Myriad Other Applications.J Biomol Tech. 2021 Sep;32(3):228-275. doi: 10.7171/jbt.21-3203-017. J Biomol Tech. 2021. PMID: 35136384 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Validation of new equipment for SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis in Ecuador: Detection of the virus and antibodies generated by disease and vaccines with one POC device.PLoS One. 2025 Apr 16;20(4):e0321794. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0321794. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40238804 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous