Loss of expression of both miR-15/16 loci in CML transition to blast crisis
- PMID: 33836616
- PMCID: PMC7980455
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2101566118
Loss of expression of both miR-15/16 loci in CML transition to blast crisis
Abstract
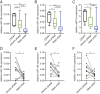
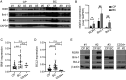
Despite advances that have improved the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) patients in chronic phase, the mechanisms of the transition from chronic phase CML to blast crisis (BC) are not fully understood. Considering the key role of miR-15/16 loci in the pathogenesis of myeloid and lymphocytic leukemia, here we aimed to correlate the expression of miR-15a/16 and miR-15b/16 to progression of CML from chronic phase to BC. We analyzed the expression of the two miR-15/16 clusters in 17 CML patients in chronic phase and 22 patients in BC and in 11 paired chronic phase and BC CML patients. BC CMLs show a significant reduction of the expression of miR-15a/-15b/16 compared to CMLs in chronic phase. Moreover, BC CMLs showed an overexpression of miR-15/16 direct targets such as Bmi-1, ROR1, and Bcl-2 compared to CMLs in chronic phase. This study highlights the loss of both miR-15/16 clusters as a potential oncogenic driver in the transition from chronic phase to BC in CML patients.
Keywords: blast crisis; chronic myeloid leukemia; miR-15/16 cluster.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
miR-96 acts as a tumor suppressor via targeting the BCR-ABL1 oncogene in chronic myeloid leukemia blastic transformation.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Nov;119:109413. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109413. Epub 2019 Sep 10. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 31518872
-
Activation of EVI1 transcription by the LEF1/β-catenin complex with p53-alteration in myeloid blast crisis of chronic myeloid leukemia.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017 Jan 22;482(4):994-1000. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.11.146. Epub 2016 Nov 28. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017. PMID: 27908728
-
RNA-Binding Protein Lin28B Promotes Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Blast Crisis by Transcriptionally Upregulating miR-181d.Mol Cancer Res. 2024 Oct 2;22(10):932-942. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-23-0928. Mol Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38847604
-
[Research advance on molecular genetics of CML blast crisis].Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2008 Feb;16(1):217-21. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2008. PMID: 18315935 Review. Chinese.
-
CML: mechanisms of disease initiation and progression.Leuk Lymphoma. 1993;11 Suppl 1:47-50. doi: 10.3109/10428199309047863. Leuk Lymphoma. 1993. PMID: 8251916 Review.
Cited by
-
Current Views on the Interplay between Tyrosine Kinases and Phosphatases in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia.Cancers (Basel). 2021 May 12;13(10):2311. doi: 10.3390/cancers13102311. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34065882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-15a targets the HSP90 co-chaperone Morgana in chronic myeloid leukemia.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 2;14(1):15089. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-65404-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38956394 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Biomarkers in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: What Have We Learned So Far?Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 19;22(22):12516. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212516. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small Non-Coding RNAs in Leukemia.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 20;14(3):509. doi: 10.3390/cancers14030509. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35158777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complete miRNA-15/16 loss in mice promotes hematopoietic progenitor expansion and a myeloid-biased hyperproliferative state.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Oct 24;120(43):e2308658120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2308658120. Epub 2023 Oct 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37844234 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Faderl S., et al. ., The biology of chronic myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 341, 164–172 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Kantarjian H. M., et al. ., Chronic myelogenous leukemia in blast crisis. Analysis of 242 patients. Am. J. Med. 83, 445–454 (1987). - PubMed
-
- Sawyers C. L., Chronic myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 340, 1330–1340 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Radich J. P., The Biology of CML blast crisis. Hematology Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2007, 384–391 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

