Poplar protease inhibitor expression differs in an herbivore specific manner
- PMID: 33836664
- PMCID: PMC8033671
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-021-02936-4
Poplar protease inhibitor expression differs in an herbivore specific manner
Abstract
Background: Protease inhibitors are defense proteins widely distributed in the plant kingdom. By reducing the activity of digestive enzymes in insect guts, they reduce the availability of nutrients and thus impair the growth and development of the attacking herbivore. One well-characterized class of protease inhibitors are Kunitz-type trypsin inhibitors (KTIs), which have been described in various plant species, including Populus spp. Long-lived woody perennials like poplar trees encounter a huge diversity of herbivores, but the specificity of tree defenses towards different herbivore species is hardly studied. We therefore aimed to investigate the induction of KTIs in black poplar (P. nigra) leaves upon herbivory by three different chewing herbivores, Lymantria dispar and Amata mogadorensis caterpillars, and Phratora vulgatissima beetles.
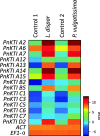
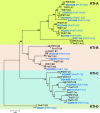
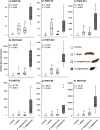
Results: We identified and generated full-length cDNA sequences of 17 KTIs that are upregulated upon herbivory in black poplar leaves, and analyzed the expression patterns of the eight most up-regulated KTIs via qRT-PCR. We found that beetles elicited higher transcriptional induction of KTIs than caterpillars, and that both caterpillar species induced similar KTI expression levels. Furthermore, KTI expression strongly correlated with the trypsin-inhibiting activity in the herbivore-damaged leaves, but was not dependent on damage severity, i.e. leaf area loss, for most of the genes.
Conclusions: We conclude that the induction of KTIs in black poplar is controlled at the transcriptional level in a threshold-based manner and is strongly influenced by the species identity of the herbivore. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms and ecological consequences of these patterns remain to be investigated.
Keywords: Coleoptera; Induced defenses; Kunitz-type trypsin inhibitors; herbivore specificity; woody plants; tree defenses; Lepidoptera; Proteinase inhibitors; Salicaceae.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Boeckler GA, Towns M, Unsicker SB, Mellway RD, Yip L, Hilke I, et al. Transgenic upregulation of the condensed tannin pathway in poplar leads to a dramatic shift in leaf palatability for two tree-feeding Lepidoptera. J Chem Ecol. 2014;40(2):150–8. 10.1007/s10886-014-0383-7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

