There is detectable variation in the lipidomic profile between stable and progressive patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF)
- PMID: 33836757
- PMCID: PMC8033725
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-021-01682-3
There is detectable variation in the lipidomic profile between stable and progressive patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF)
Abstract
Background: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a chronic interstitial lung disease characterized by fibrosis and progressive loss of lung function. The pathophysiological pathways involved in IPF are not well understood. Abnormal lipid metabolism has been described in various other chronic lung diseases including asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). However, its potential role in IPF pathogenesis remains unclear.
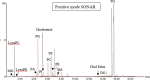
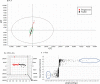
Methods: In this study, we used ultra-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-QTOF-MS) to characterize lipid changes in plasma derived from IPF patients with stable and progressive disease. We further applied a data-independent acquisition (DIA) technique called SONAR, to improve the specificity of lipid identification.
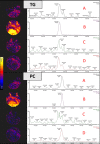
Results: Statistical modelling showed variable discrimination between the stable and progressive subjects, revealing differences in the detection of triglycerides (TG) and phosphatidylcholines (PC) between progressors and stable IPF groups, which was further confirmed by mass spectrometry imaging (MSI) in IPF tissue.
Conclusion: This is the first study to characterise lipid metabolism between stable and progressive IPF, with results suggesting disparities in the circulating lipidome with disease progression.
Keywords: DIA; IPF; Lipids; MS; Plasma; SONAR.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of the lipid biomarkers from plasma in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis by Lipidomics.BMC Pulm Med. 2017 Dec 6;17(1):174. doi: 10.1186/s12890-017-0513-4. BMC Pulm Med. 2017. PMID: 29212488 Free PMC article.
-
Untargeted metabolomics of human plasma reveal lipid markers unique to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Proteomics Clin Appl. 2021 May;15(2-3):e2000039. doi: 10.1002/prca.202000039. Epub 2021 Mar 18. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2021. PMID: 33580915
-
Serum metabolic profiling identified a distinct metabolic signature in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis - a potential biomarker role for LysoPC.Respir Res. 2018 Jan 10;19(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s12931-018-0714-2. Respir Res. 2018. PMID: 29321022 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Lipid metabolism in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: From pathogenesis to therapy.J Mol Med (Berl). 2023 Aug;101(8):905-915. doi: 10.1007/s00109-023-02336-1. Epub 2023 Jun 8. J Mol Med (Berl). 2023. PMID: 37289208 Review.
-
Lipid Mediators Regulate Pulmonary Fibrosis: Potential Mechanisms and Signaling Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 15;21(12):4257. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124257. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32549377 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Succinate promotes pulmonary fibrosis through GPR91 and predicts death in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 22;14(1):14376. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-64844-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38909094 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in serum metabolomics in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and effect of approved antifibrotic medication.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 17;13:837680. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.837680. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36059968 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical value of triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio for predicting stroke-associated pneumonia after spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage.BMC Neurol. 2025 Apr 9;25(1):148. doi: 10.1186/s12883-025-04154-z. BMC Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40205549 Free PMC article.
-
PPARG/SPP1/CD44 signaling pathway in alveolar macrophages: Mechanisms of lipid dysregulation and therapeutic targets in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Heliyon. 2025 Jan 2;11(1):e41628. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e41628. eCollection 2025 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 39866448 Free PMC article.
-
Novel lipidomes profile and clinical phenotype identified in pneumoconiosis patients.J Health Popul Nutr. 2023 Jun 15;42(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s41043-023-00400-7. J Health Popul Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37322561 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

