In utero exposure to chlordecone affects histone modifications and activates LINE-1 in cord blood
- PMID: 33837044
- PMCID: PMC8091598
- DOI: 10.26508/lsa.202000944
In utero exposure to chlordecone affects histone modifications and activates LINE-1 in cord blood
Abstract
Environmental factors can induce detrimental consequences into adulthood life. In this study, we examined the epigenetic effects induced by in utero chlordecone (CD) exposure on human male cord blood as well as in blood-derived Ke-37 cell line. Genome-wide analysis of histone H3K4me3 distribution revealed that genes related to chromosome segregation, chromatin organization, and cell cycle have altered occupancy in their promoters. The affected regions were enriched in ESR1, SP family, and IKZF1 binding motifs. We also observed a global reduction in H3K9me3, markedly in repeated sequences of the genome. Decrease in H3K9me3 after CD exposure correlates with decreased methylation in LINE-1 promoters and telomere length extension. These observations on human cord blood were assessed in the Ke-37 human cell line. H3K4me3 and the expression of genes related to immune response, DNA repair, and chromatin organization, which were affected in human cord blood were also altered in CD-exposed Ke-37 cells. Our data suggest that developmental exposure to CD leads to profound changes in histone modification patterns and affects the processes controlled by them in human cord blood.
© 2021 Legoff et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


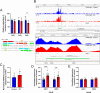
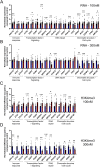
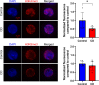
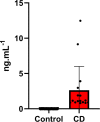
References
-
- Morales E, Vilahur N, Salas LA, Motta V, Fernandez MF, Murcia M, Llop S, Tardon A, Fernandez-Tardon G, Santa-Marina L, et al. (2016) Genome-wide DNA methylation study in human placenta identifies novel loci associated with maternal smoking during pregnancy. Int J Epidemiol 45: 1644–1655. 10.1093/ije/dyw196 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
