WBP2 negatively regulates the Hippo pathway by competitively binding to WWC3 with LATS1 to promote non-small cell lung cancer progression
- PMID: 33837178
- PMCID: PMC8035140
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-021-03600-3
WBP2 negatively regulates the Hippo pathway by competitively binding to WWC3 with LATS1 to promote non-small cell lung cancer progression
Abstract
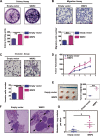
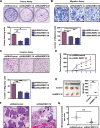
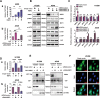
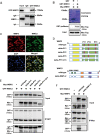
WW domain binding protein-2 (WBP2) can function as a Yes-associated protein/transcriptional co-activator with PDZ-binding motif (YAP/TAZ) co-activator and has a crucial role in promoting breast cancer progression. However, the expression and potential molecular mechanisms of WBP2 in the context of lung cancer are not fully understood. We determined that WBP2 was highly expressed in lung cancer specimens and cell lines and that this expression was closely related to the advanced pTNM stage, lymph node metastasis, and poor prognosis of patients. In addition, gain- and loss-of-function experiments revealed that WBP2 could significantly promote the proliferation and invasion of lung cancer cells both in vivo and in vitro. To elucidate the underlying molecular mechanism, we determined that wild-type WBP2 could competitively bind to the WW domain of WWC3 (WW and C2 domain-containing-3) with LATS1 (Large tumor suppressor-1) through its PPxY motifs, thus inhibiting the formation of the WWC3-LATS1 complex, reducing the phosphorylation level of LATS1, suppressing the activity of the Hippo pathway, and ultimately promoting YAP nuclear translocation. Therefore, from the aspect of upstream molecules of Hippo signaling, WBP2 promotes the malignant phenotype of lung cancer cells in a unique manner that is not directly dependent upon YAP, thus providing a corresponding experimental basis for the development of targeted therapeutic drugs for lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Reciprocal Regulation of Hippo and WBP2 Signalling-Implications in Cancer Therapy.Cells. 2021 Nov 11;10(11):3130. doi: 10.3390/cells10113130. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
WWC3 regulates the Wnt and Hippo pathways via Dishevelled proteins and large tumour suppressor 1, to suppress lung cancer invasion and metastasis.J Pathol. 2017 Aug;242(4):435-447. doi: 10.1002/path.4919. Epub 2017 Jun 29. J Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28543074
-
WW domain-mediated interaction with Wbp2 is important for the oncogenic property of TAZ.Oncogene. 2011 Feb 3;30(5):600-10. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.438. Epub 2010 Oct 25. Oncogene. 2011. PMID: 20972459 Free PMC article.
-
WWC3 inhibits intimal proliferation following vascular injury via the Hippo signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Apr;17(4):5175-5183. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8484. Epub 2018 Jan 25. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29393412 Free PMC article.
-
Reciprocal regulation of YAP/TAZ by the Hippo pathway and the Small GTPase pathway.Small GTPases. 2020 Jul;11(4):280-288. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2018.1435986. Epub 2018 Apr 20. Small GTPases. 2020. PMID: 29457552 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
WBP2 promotes BTRC mRNA stability to drive migration and invasion in triple-negative breast cancer via NF-κB activation.Mol Oncol. 2022 Jan;16(2):422-446. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13048. Epub 2021 Aug 12. Mol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 34197030 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT1 silencing ameliorates malignancy of non-small cell lung cancer via activating FOXO1.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 28;14(1):19948. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70970-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39198693 Free PMC article.
-
Reciprocal Regulation of Hippo and WBP2 Signalling-Implications in Cancer Therapy.Cells. 2021 Nov 11;10(11):3130. doi: 10.3390/cells10113130. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The components and regulation of the Hippo pathway and its relationships with the progression and treatment of Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Cancer Cell Int. 2025 Aug 20;25(1):309. doi: 10.1186/s12935-025-03946-0. Cancer Cell Int. 2025. PMID: 40830878 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TMEM120B strengthens breast cancer cell stemness and accelerates chemotherapy resistance via β1-integrin/FAK-TAZ-mTOR signaling axis by binding to MYH9.Breast Cancer Res. 2024 Mar 19;26(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s13058-024-01802-z. Breast Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38504374 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

