Improved prime editors enable pathogenic allele correction and cancer modelling in adult mice
- PMID: 33837189
- PMCID: PMC8035190
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-22295-w
Improved prime editors enable pathogenic allele correction and cancer modelling in adult mice
Abstract
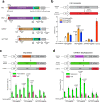
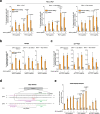
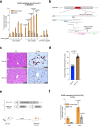
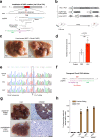
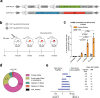
Prime editors (PEs) mediate genome modification without utilizing double-stranded DNA breaks or exogenous donor DNA as a template. PEs facilitate nucleotide substitutions or local insertions or deletions within the genome based on the template sequence encoded within the prime editing guide RNA (pegRNA). However, the efficacy of prime editing in adult mice has not been established. Here we report an NLS-optimized SpCas9-based prime editor that improves genome editing efficiency in both fluorescent reporter cells and at endogenous loci in cultured cell lines. Using this genome modification system, we could also seed tumor formation through somatic cell editing in the adult mouse. Finally, we successfully utilize dual adeno-associated virus (AAVs) for the delivery of a split-intein prime editor and demonstrate that this system enables the correction of a pathogenic mutation in the mouse liver. Our findings further establish the broad potential of this genome editing technology for the directed installation of sequence modifications in vivo, with important implications for disease modeling and correction.
Conflict of interest statement
UMass has filed a patent application on PE2* and AAT pegRNAs in this work (inventors: P.L., S.Q.L., S.A.W., and W.X., patent filed/pending). S.A.W. is a consultant for Chroma Medicine. All remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of a commercial or financial conflict of interest. The authors declare no competing non-financial interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

