Actionable druggable genome-wide Mendelian randomization identifies repurposing opportunities for COVID-19
- PMID: 33837377
- PMCID: PMC7612986
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-021-01310-z
Actionable druggable genome-wide Mendelian randomization identifies repurposing opportunities for COVID-19
Abstract
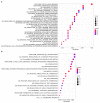
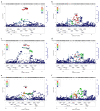
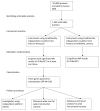
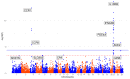
Drug repurposing provides a rapid approach to meet the urgent need for therapeutics to address COVID-19. To identify therapeutic targets relevant to COVID-19, we conducted Mendelian randomization analyses, deriving genetic instruments based on transcriptomic and proteomic data for 1,263 actionable proteins that are targeted by approved drugs or in clinical phase of drug development. Using summary statistics from the Host Genetics Initiative and the Million Veteran Program, we studied 7,554 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 and >1 million controls. We found significant Mendelian randomization results for three proteins (ACE2, P = 1.6 × 10-6; IFNAR2, P = 9.8 × 10-11 and IL-10RB, P = 2.3 × 10-14) using cis-expression quantitative trait loci genetic instruments that also had strong evidence for colocalization with COVID-19 hospitalization. To disentangle the shared expression quantitative trait loci signal for IL10RB and IFNAR2, we conducted phenome-wide association scans and pathway enrichment analysis, which suggested that IFNAR2 is more likely to play a role in COVID-19 hospitalization. Our findings prioritize trials of drugs targeting IFNAR2 and ACE2 for early management of COVID-19.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Nelson MR, et al. The support of human genetic evidence for approved drug indications. Nat Genet. 2015;47:856–860. - PubMed
-
- Cohen JC, Boerwinkle E, Mosley TH, Jr, Hobbs HH. Sequence variations in PCSK9, low LDL, and protection against coronary heart disease. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:1264–1272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

