COVID-19: imbalance of multiple systems during infection and importance of therapeutic choice and dosing of cardiac and anti-coagulant therapies
- PMID: 33837899
- PMCID: PMC8035598
- DOI: 10.1007/s11033-021-06333-w
COVID-19: imbalance of multiple systems during infection and importance of therapeutic choice and dosing of cardiac and anti-coagulant therapies
Abstract
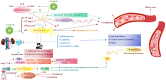
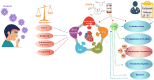
The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and its metabolites play an important role in homeostasis of body, especially the cardiovascular system. In this study, we discuss the imbalance of multiple systems during the infection and the importance of therapeutic choice, dosing, and laboratory monitoring of cardiac and anti-coagulant therapies in COVID-19 patients. The crosstalk between angiotensin, kinin-kallikrein system, as well as inflammatory and coagulation systems plays an essential role in COVID-19. Cardiac complications and coagulopathies imply the crosstalks between the mentioned systems. We believe that the blockage of bradykinin can be a good option in the management of COVID-19 and CVD in patients and that supportive treatment of respiratory and cardiologic complications is needed in COVID-19 patients. Ninety-one percent of COVID-19 patients who were admitted to hospital with a prolonged aPTT were positive for lupus anticoagulant, which increases the risk of thrombosis and prolonged aPTT. Therefore, the question that is posed at this juncture is whether it is safe to use the prophylactic dose of heparin particularly in those with elevated D-dimer levels. It should be noted that timing is of high importance in anti-coagulant therapy; therefore, we should consider the level of D-dimer, fibrinogen, drug-drug interactions, and risk factors during thromboprophylaxis administration. Fibrinogen is an independent predictor of resistance to heparin and should be considered before thromboprophylaxis. Alteplase and Futhan might be a good choice to assess the condition of heparin resistance. Finally, the treatment option, dosing, and laboratory monitoring of anticoagulant therapy are critical decisions in COVID-19 patients.
Keywords: Bradykinin; Cardiac complications; Coagulation; Cytokine storm; SARS-CoV-2.
Conflict of interest statement
This manuscript is a review article and does not involve a research protocol requiring approval by the relevant institutional review board or ethics committee. Authors declare no complicit of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Cytokine/Bradykinin Storm Comparison: What Is the Relationship Between Hypertension and COVID-19?Am J Hypertens. 2021 Apr 20;34(4):304-306. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpaa217. Am J Hypertens. 2021. PMID: 33877321 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Thrombocytopenia and thrombosis in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.J Hematol Oncol. 2020 Dec 1;13(1):161. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-01003-z. J Hematol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33261634 Free PMC article.
-
Mathematical Modeling of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection Network with Cytokine Storm, Oxidative Stress, Thrombosis, Insulin Resistance, and Nitric Oxide Pathways.OMICS. 2021 Dec;25(12):770-781. doi: 10.1089/omi.2021.0155. Epub 2021 Nov 22. OMICS. 2021. PMID: 34807729
-
Anticoagulation for COVID-19 Patients: A Bird's-Eye View.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2021 Jan-Dec;27:10760296211039288. doi: 10.1177/10760296211039288. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2021. PMID: 34595937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of kallikrein-kinin and renin-angiotensin systems in COVID-19 infection.Peptides. 2021 Jan;135:170428. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2020.170428. Epub 2020 Oct 14. Peptides. 2021. PMID: 33065209 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Review of the Potential Roles of Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Pharmacological Approaches for the Management of Mild-to-Moderate Symptomatic COVID-19.Med Sci Monit. 2022 Mar 8;28:e936292. doi: 10.12659/MSM.936292. Med Sci Monit. 2022. PMID: 35256581 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperinflammatory Response in COVID-19: A Systematic Review.Viruses. 2023 Feb 16;15(2):553. doi: 10.3390/v15020553. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36851766 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence and Risk Factors Associated with Thromboembolic Events among Patients with COVID-19 Inpatients: A Retrospective Study.Indian J Crit Care Med. 2023 Nov;27(11):830-836. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10071-24575. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2023. PMID: 37936799 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

