Shutoff of host transcription triggers a toxin-antitoxin system to cleave phage RNA and abort infection
- PMID: 33838104
- PMCID: PMC8284924
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.03.027
Shutoff of host transcription triggers a toxin-antitoxin system to cleave phage RNA and abort infection
Abstract
Toxin-antitoxin (TA) systems are widespread in bacteria, but their activation mechanisms and bona fide targets remain largely unknown. Here, we characterize a type III TA system, toxIN, that protects E. coli against multiple bacteriophages, including T4. Using RNA sequencing, we find that the endoribonuclease ToxN is activated following T4 infection and blocks phage development primarily by cleaving viral mRNAs and inhibiting their translation. ToxN activation arises from T4-induced shutoff of host transcription, specifically of toxIN, leading to loss of the intrinsically unstable toxI antitoxin. Transcriptional shutoff is necessary and sufficient for ToxN activation. Notably, toxIN does not strongly protect against another phage, T7, which incompletely blocks host transcription. Thus, our results reveal a critical trade-off in blocking host transcription: it helps phage commandeer host resources but can activate potent defense systems. More generally, our results now reveal the native targets of an RNase toxin and activation mechanism of a phage-defensive TA system.
Keywords: E. coli; T4 phage; bacterial transcription; endoribonuclease; phage defense; toxin-antitoxin.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
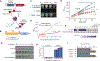
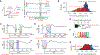
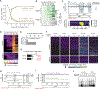

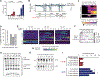
Similar articles
-
A phage-encoded RNA-binding protein inhibits the antiviral activity of a toxin-antitoxin system.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Feb 9;52(3):1298-1312. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad1207. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38117986 Free PMC article.
-
Global Analysis of the Specificities and Targets of Endoribonucleases from Escherichia coli Toxin-Antitoxin Systems.mBio. 2021 Oct 26;12(5):e0201221. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02012-21. Epub 2021 Sep 21. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34544284 Free PMC article.
-
RnlB Antitoxin of the Escherichia coli RnlA-RnlB Toxin-Antitoxin Module Requires RNase HI for Inhibition of RnlA Toxin Activity.Toxins (Basel). 2017 Jan 11;9(1):29. doi: 10.3390/toxins9010029. Toxins (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28085056 Free PMC article.
-
Xenogeneic Regulation of the Bacterial Transcription Machinery.J Mol Biol. 2019 Sep 20;431(20):4078-4092. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.02.008. Epub 2019 Feb 15. J Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30776429 Review.
-
Ribonucleases in bacterial toxin-antitoxin systems.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jun-Jul;1829(6-7):523-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2013.02.007. Epub 2013 Feb 21. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23454553 Review.
Cited by
-
The evolution of a counter-defense mechanism in a virus constrains its host range.Elife. 2022 Aug 4;11:e79549. doi: 10.7554/eLife.79549. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35924892 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial defense systems exhibit synergistic anti-phage activity.Cell Host Microbe. 2024 Apr 10;32(4):557-572.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2024.01.015. Epub 2024 Feb 22. Cell Host Microbe. 2024. PMID: 38402614 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-phage defence through inhibition of virion assembly.Nat Commun. 2024 Feb 22;15(1):1644. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45892-x. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38388474 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogeny Reveals Novel HipA-Homologous Kinase Families and Toxin-Antitoxin Gene Organizations.mBio. 2021 Jun 29;12(3):e0105821. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01058-21. Epub 2021 Jun 1. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34061596 Free PMC article.
-
A phage-encoded RNA-binding protein inhibits the antiviral activity of a toxin-antitoxin system.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Feb 9;52(3):1298-1312. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad1207. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38117986 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blower TR, Chai R, Przybilski R, Chindhy S, Fang X, Kidman SE, Tan H, Luisi BF, Fineran PC, and Salmond GPC (2017). Evolution of Pectobacterium Bacteriophage ΦM1 To Escape Two Bifunctional Type III Toxin-Antitoxin and Abortive Infection Systems through Mutations in a Single Viral Gene. Appl Environ Microb 83, e03229–16. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brunovskis I, and Summers WC (1971). The process of infection with coliphage T7 V. Shutoff of host RNA synthesis by an early phage function. Virology 45, 224–231. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

