Organoid modeling of Zika and herpes simplex virus 1 infections reveals virus-specific responses leading to microcephaly
- PMID: 33838105
- PMCID: PMC7611471
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2021.03.004
Organoid modeling of Zika and herpes simplex virus 1 infections reveals virus-specific responses leading to microcephaly
Abstract
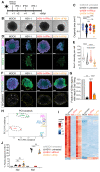
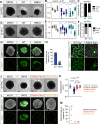
Viral infection in early pregnancy is a major cause of microcephaly. However, how distinct viruses impair human brain development remains poorly understood. Here we use human brain organoids to study the mechanisms underlying microcephaly caused by Zika virus (ZIKV) and herpes simplex virus (HSV-1). We find that both viruses efficiently replicate in brain organoids and attenuate their growth by causing cell death. However, transcriptional profiling reveals that ZIKV and HSV-1 elicit distinct cellular responses and that HSV-1 uniquely impairs neuroepithelial identity. Furthermore, we demonstrate that, although both viruses fail to potently induce the type I interferon system, the organoid defects caused by their infection can be rescued by distinct type I interferons. These phenotypes are not seen in 2D cultures, highlighting the superiority of brain organoids in modeling viral infections. These results uncover virus-specific mechanisms and complex cellular immune defenses associated with virus-induced microcephaly.
Keywords: Zika virus; brain organoids; herpes simplex virus; innate immune response; interferons; microcephaly; neural progenitors; neuroepithelial polarity.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests J.A.K. is inventor on a patent describing cerebral organoid technology and co-founder and scientific advisory board member of a:head bio AG.
Figures
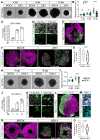
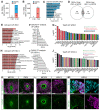

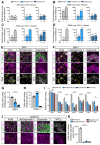
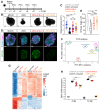
References
-
- Amin ND, Paşca SP. Building Models of Brain Disorders with Three-Dimensional Organoids. Neuron. 2018;100:389–405. - PubMed
-
- Arao Y, Ando Y, Narita M, Kurata T. Unexpected correlation in the sensitivity of 19 herpes simplex virus strains to types I and II interferons. Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research. 1997;17:537–541. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

