A Novel Role of Claudin-5 in Prevention of Mitochondrial Fission Against Ischemic/Hypoxic Stress in Cardiomyocytes
- PMID: 33838228
- PMCID: PMC8497653
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cjca.2021.03.021
A Novel Role of Claudin-5 in Prevention of Mitochondrial Fission Against Ischemic/Hypoxic Stress in Cardiomyocytes
Abstract
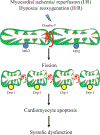
Background: Downregulation of claudin-5 in the heart is associated with the end-stage heart failure. However, the underlying mechanism ofclaudin-5 is unclear. Here we investigated the molecular actions of claudin-5 in perspective of mitochondria in cardiomyocytes to better understand the role of claudin-5 in cardioprotection during ischemia.
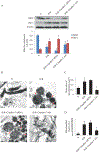
Methods: Myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R; 30 min/24 h) and hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R; 24 h/4 h) were used in this study. Confocal microscopy and transmission electron microscope (TEM) were used to observe mitochondrial morphology.
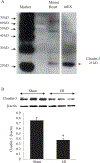
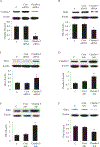
Results: Claudin-5 was detected in murine heart tissue and neonatal rat cardiomyocytes (NRCM). Its protein level was severely decreased after myocardial I/R or H/R. Confocal microscopy showedclaudin-5 presented in the mitochondria of NRCM. H/R-induced claudin-5 downregulation was accompanied by mitochondrial fragmentation. The mitofusin 2 (Mfn2) expressionwas dramatically decreased while the dynamin-related protein (Drp) 1 expression was significantly increased after H/R. The TEM indicatedH/R-induced mitochondrial swelling and fission. Adenoviral claudin-5 overexpression reversed these structural disintegration of mitochondria. The mitochondria-centered intrinsic pathway of apoptosis triggered by H/R and indicated by the cytochrome c and cleaved caspase 3 in the cytoplasm of NRCMs was also reduced by overexpressing claudin-5. Claudin-5 overexpression in mouse heart also significantly decreased cleaved caspase 3 and the infarct size in ischemic heart with improved systolic function.
Conclusion: We demonstrated for the first time the presence of claudin-5 in the mitochondria in cardiomyocytes and provided the firm evidence for the cardioprotective role of claudin-5 in the preservation of mitochondrial dynamics and cell fate against hypoxia- or ischemia-induced stress.
Copyright © 2021 Canadian Cardiovascular Society. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Taddei A, Giampietro C, Conti A, et al. Endothelial adherens junctions control tight junctions by VE-cadherin-mediated upregulation of claudin-5. Nature cell biology. 2008;10:923–934. - PubMed
-
- Huang P, Zhou CM, Qin H, et al. Cerebralcare Granule(R) attenuates blood-brain barrier disruption after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Experimental neurology. 2012;237:453–463. - PubMed
-
- Kashiwamura Y, Sano Y, Abe M, et al. Hydrocortisone enhances the function of the blood-nerve barrier through the up-regulation of claudin-5. Neurochemical research. 2011;36:849–855. - PubMed
-
- Zhu H, Wang Z, Xing Y, et al. Baicalin reduces the permeability of the blood-brain barrier during hypoxia in vitro by increasing the expression of tight junction proteins in brain microvascular endothelial cells. Journal of ethnopharmacology. 2012;141:714–720. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

