Vergence, accommodation, and visual tracking in children and adolescents evaluated in a multidisciplinary concussion clinic
- PMID: 33838503
- PMCID: PMC8145776
- DOI: 10.1016/j.visres.2021.03.002
Vergence, accommodation, and visual tracking in children and adolescents evaluated in a multidisciplinary concussion clinic
Abstract
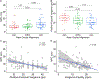
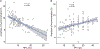
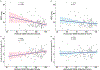
Many patients with concussion experience visual symptoms following injury that lead to a diagnosis of convergence insufficiency, accommodative insufficiency, or saccadic dysfunction. However, these diagnostic categories are based on aggregates of clinical tests developed from a non-concussed population and therefore may not accurately describe visual deficits in the concussed population. Thus, we sought to understand individual metrics of visual dysfunction in chronically symptomatic post-concussion patients. This retrospective cross-sectional study included patients examined at the multidisciplinary concussion clinic (MDCC) at Boston Children's Hospital over four years. Patients aged 5-21 years who had a complete assessment of eye alignment, vergence, accommodation, and visual tracking, and had visual acuity better than or equal to 20/30 in each eye were included. Patients with history of amblyopia, strabismus, or ocular pathology were excluded. Chart review yielded 116 patients who met inclusion criteria (median age 15 years, 64% female). The majority of patients (52%) experienced a single concussion and most were sports-related (50%). Clinical data show vergence, accommodation, or visual tracking deficits in 95% of patients. A receded near point of convergence (NPC, 70/116) and reduced accommodative amplitude (63/116) were the most common deficits. Both NPC and accommodative amplitude were significantly correlated with one another (r = -0.5) and with measures of visual tracking (r = -0.34). Patients with chronic post-concussion symptoms show deficits in individual metrics of vergence, accommodation and visual tracking. The high incidence of these deficits, specifically NPC and accommodative amplitude, highlights the need for a detailed sensorimotor evaluation to guide personalized treatment following concussion.
Keywords: Accommodation; Binocular vision; Concussion; Vergence; Visual tracking.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
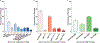
Similar articles
-
Vergence and accommodation deficits in paediatric and adolescent patients during sub-acute and chronic phases of concussion recovery.Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2024 Sep;44(6):1091-1099. doi: 10.1111/opo.13346. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2024. PMID: 38853693
-
Postconcussion: Receded Near Point of Convergence is not Diagnostic of Convergence Insufficiency.Am J Ophthalmol. 2019 Oct;206:235-244. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2019.04.008. Epub 2019 Apr 17. Am J Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 31004592
-
Frequency of oculomotor disorders in adolescents 11 to 17 years of age with concussion, 4 to 12 weeks post injury.Vision Res. 2021 Jun;183:73-80. doi: 10.1016/j.visres.2020.09.011. Epub 2021 Mar 15. Vision Res. 2021. PMID: 33735759
-
Diagnostic Protocol for Accommodative and Vergence Anomalies - A Review.J Binocul Vis Ocul Motil. 2024 Apr-Jun;74(2):48-64. doi: 10.1080/2576117X.2024.2347663. Epub 2024 Jun 20. J Binocul Vis Ocul Motil. 2024. PMID: 38899986 Review.
-
Influence of accommodative and vergence adaptation on binocular motor disorders.Am J Optom Physiol Opt. 1988 Jun;65(6):464-75. doi: 10.1097/00006324-198806000-00006. Am J Optom Physiol Opt. 1988. PMID: 3046365 Review.
Cited by
-
Trajectories of Visual and Vestibular Markers of Youth Concussion.J Neurotrauma. 2022 Oct;39(19-20):1382-1390. doi: 10.1089/neu.2022.0014. J Neurotrauma. 2022. PMID: 35785959 Free PMC article.
-
Scoping review: Intervention for ocular motor disorders in children and adults with mild traumatic brain injury.Optom Vis Sci. 2025 Apr 1;102(4):204-214. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0000000000002237. Epub 2025 Feb 14. Optom Vis Sci. 2025. PMID: 39951336 Free PMC article.
-
Visual Dysfunctions in Mild Traumatic Brain Injury: A Focus on Accommodative System Impairments.Life (Basel). 2025 May 6;15(5):744. doi: 10.3390/life15050744. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40430172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Accommodative and Vergence Responses to a Moving Stimulus in Concussion.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2024 Oct 1;65(12):45. doi: 10.1167/iovs.65.12.45. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2024. PMID: 39475939 Free PMC article.
-
OculoMotor & Vestibular Endurance Screening (MoVES) Normative, Repeatability, and Reliability Data.Brain Sci. 2024 Jul 14;14(7):704. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14070704. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 39061444 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agarwal M, Ulmer JL, Chandra T, Klein AP, Mark LP, & Mohan S (2016). Imaging correlates of neural control of ocular movements. European Radiology, 26(7), 2193–2205. - PubMed
-
- Ciuffreda KJ, Kapoor N, Rutner D, Suchoff IB, Han ME, & Craig S (2007). Occurrence of oculomotor dysfunctions in acquired brain injury: a retrospective analysis. Optometry, 78(4), 155–161. - PubMed
-
- Ciuffreda KJ, & Ludlam DP (2011). Conceptual model of optometric vision care in mild traumatic brain injury. J Behav Optom. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Diana_Ludlam/publication/268172783_...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

