Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor and mortality in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) - A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression
- PMID: 33838614
- PMCID: PMC8012165
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dsx.2021.03.027
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor and mortality in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) - A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression
Abstract
Background and aims: This study aims to synthesize evidence on dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor and mortality in COVID-19 patients and factors affecting it.
Methods: We performed a systematic literature search from PubMed, Scopus, and Embase databases from inception of databases up until 7 March 2021. Studies that met all of the following criteria were included: 1) observational studies or randomized controlled trials that report COVID-19 patients, 2) reporting DPP-4 inhibitor use, 3) mortality, and 4) mortality based on DPP-4 inhibitor use. The exposure was DPP-4 inhibitor, defined as DPP-4 inhibitor use that started prior to COVID-19 hospitalization. The control group was patients with no exposure to DPP-4 inhibitor. The outcome was mortality. The pooled effect estimate was reported as risk ratio (RR).
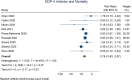
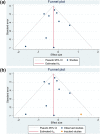
Results: There were 4,477 patients from 9 studies in this systematic review and meta-analysis. 31% of (15%, 46%) the patients use DPP-4 inhibitor. Mortality occurs in 23% (15%, 31%) of the patients. DPP-4 inhibitor was associated with lower mortality in patients with COVID-19 (RR 0.76 [0.60, 0.97], p = 0.030, I2: 44.5%, p = 0.072). Meta-regression analysis showed that the association between DPP-4 inhibitor and mortality was significantly affected by metformin (RR 1.02 [1.00, 1.04], p = 0.048) and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker (ACEI/ARB) use (RR 1.04 [1.01, 1.07], p = 0.006), but not age (p = 0.759), sex (reference: male, p = 0.148), and hypertension (p = 0.218).
Conclusion: DPP-4 inhibitor use was associated with lower mortality in COVID-19 patients, and the association was weaker in patients who were also taking metformin and/or ACE inhibitors.
Keywords: COVID-19; Diabetes; Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor; Mortality; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2021 Diabetes India. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest None.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . 2021. Weekly epidemiological update - 9 February 2021. Geneva.
-
- Huang I., Lim M.A., Pranata R. Diabetes mellitus is associated with increased mortality and severity of disease in COVID-19 pneumonia – a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression: diabetes and COVID-19. Diabetes Metab Syndr Clin Res Rev. 2020;14:395–403. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.018. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous