Chemokines and the immune response to cancer
- PMID: 33838745
- PMCID: PMC8434759
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2021.01.012
Chemokines and the immune response to cancer
Abstract
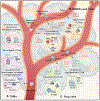
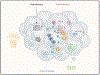
Chemokines are chemotactic cytokines that regulate the migration of immune cells. Chemokines function as cues for the coordinated recruitment of immune cells into and out of tissue and also guide the spatial organization and cellular interactions of immune cells within tissues. Chemokines are critical in directing immune cell migration necessary to mount and then deliver an effective anti-tumor immune response; however, chemokines also participate in the generation and recruitment of immune cells that contribute to a pro-tumorigenic microenvironment. Here, we review the role of the chemokine system in anti-tumor and pro-tumor immune responses and discuss how malignant cells and the tumor microenvironment regulate the overall chemokine landscape to shape the type and outcome of immune responses to cancer and cancer treatment.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Balkwill F (2004). Cancer and the chemokine network. Nat. Rev. Cancer 4, 540–550. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

