Age-associated proinflammatory elastic fiber remodeling in large arteries
- PMID: 33839189
- PMCID: PMC8154723
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mad.2021.111490
Age-associated proinflammatory elastic fiber remodeling in large arteries
Abstract
Elastic fibers are the main components of the extracellular matrix of the large arterial wall. Elastic fiber remodeling is an intricate process of synthesis and degradation of the core elastin protein and microfibrils accompanied by the assembly and disassembly of accessory proteins. Age-related morphological, structural, and functional proinflammatory remodeling within the elastic fiber has a profound effect upon the integrity, elasticity, calcification, amyloidosis, and stiffness of the large arterial wall. An age-associated increase in arterial stiffness is a major risk factor for the pathogenesis of diseases of the large arteries such as hypertensive and atherosclerotic vasculopathy. This mini review is an update on the key molecular, cellular, functional, and structural mechanisms of elastic fiber proinflammatory remodeling in large arteries with aging. Targeting structural and functional integrity of the elastic fiber may be an effective approach to impede proinflammatory arterial remodeling with advancing age.
Keywords: Aging; Elastic fibers; Large artery; Proinflammation.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
None
Figures
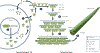
Similar articles
-
Unraveling Elastic Fiber-Derived Signaling in Arterial Aging and Related Arterial Diseases.Biomolecules. 2025 Jan 21;15(2):153. doi: 10.3390/biom15020153. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40001457 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proinflammatory Arterial Stiffness Syndrome: A Signature of Large Arterial Aging.J Vasc Res. 2018;55(4):210-223. doi: 10.1159/000490244. Epub 2018 Aug 2. J Vasc Res. 2018. PMID: 30071538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elastin in large artery stiffness and hypertension.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2012 Jun;5(3):264-73. doi: 10.1007/s12265-012-9349-8. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2012. PMID: 22290157 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Codependence of Bone Morphogenetic Protein Receptor 2 and Transforming Growth Factor-β in Elastic Fiber Assembly and Its Perturbation in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017 Aug;37(8):1559-1569. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.309696. Epub 2017 Jun 15. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017. PMID: 28619995 Free PMC article.
-
Elastic tissue disruption is a major pathogenic factor to human vascular disease.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 May;48(5):4865-4878. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06478-8. Epub 2021 Jun 15. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34129188 Review.
Cited by
-
Echocardiographic Phenotypes of Subclinical Organ Damage: Clinical and Prognostic Value in the General Population. Findings from the Pamela Study.High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2023 Nov;30(6):497-511. doi: 10.1007/s40292-023-00610-4. Epub 2023 Nov 30. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2023. PMID: 38032423 Review.
-
Inflammatory Role of Milk Fat Globule-Epidermal Growth Factor VIII in Age-Associated Arterial Remodeling.J Am Heart Assoc. 2022 Sep 6;11(17):e022574. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.121.022574. Epub 2022 Aug 24. J Am Heart Assoc. 2022. PMID: 36000422 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of puerarin on chronic inflammation: Focus on the heart, brain, and arteries.Aging Med (Milton). 2021 Dec 15;4(4):317-324. doi: 10.1002/agm2.12189. eCollection 2021 Dec. Aging Med (Milton). 2021. PMID: 34964013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is Thoracic Aortic Diameter an Independent Predictor of Cardiovascular Disease and Mortality? A Narrative Review.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Apr 29;9:867026. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.867026. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35571154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Environmental and genetic predictors of human cardiovascular ageing.Nat Commun. 2023 Aug 21;14(1):4941. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40566-6. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37604819 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angel PM, Narmoneva DA, Sewell-Loftin MK, Munjal C, Dupuis L, Landis BJ, Jegga A, Kern CB, Merryman WD, Baldwin HS, Bressan GM, Hinton RB, 2017. Proteomic Alterations Associated with Biomechanical Dysfunction are Early Processes in the Emilin1 Deficient Mouse Model of Aortic Valve Disease. Ann Biomed Eng 45, 2548–2562. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Annovi G, Boraldi F, Moscarelli P, Guerra D, Tiozzo R, Parma B, Sommer P, Quaglino D, 2012. Heparan sulfate affects elastin deposition in fibroblasts cultured from donors of different ages. Rejuvenation Res 15, 22–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

