Bioinformatics and machine learning approach identifies potential drug targets and pathways in COVID-19
- PMID: 33839760
- PMCID: PMC8083354
- DOI: 10.1093/bib/bbab120
Bioinformatics and machine learning approach identifies potential drug targets and pathways in COVID-19
Abstract
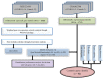
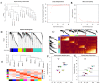
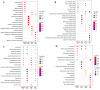
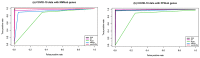
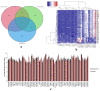
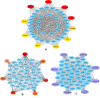
Current coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has caused massive loss of lives. Clinical trials of vaccines and drugs are currently being conducted around the world; however, till now no effective drug is available for COVID-19. Identification of key genes and perturbed pathways in COVID-19 may uncover potential drug targets and biomarkers. We aimed to identify key gene modules and hub targets involved in COVID-19. We have analyzed SARS-CoV-2 infected peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) transcriptomic data through gene coexpression analysis. We identified 1520 and 1733 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) from the GSE152418 and CRA002390 PBMC datasets, respectively (FDR < 0.05). We found four key gene modules and hub gene signature based on module membership (MMhub) statistics and protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks (PPIhub). Functional annotation by enrichment analysis of the genes of these modules demonstrated immune and inflammatory response biological processes enriched by the DEGs. The pathway analysis revealed the hub genes were enriched with the IL-17 signaling pathway, cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction pathways. Then, we demonstrated the classification performance of hub genes (PLK1, AURKB, AURKA, CDK1, CDC20, KIF11, CCNB1, KIF2C, DTL and CDC6) with accuracy >0.90 suggesting the biomarker potential of the hub genes. The regulatory network analysis showed transcription factors and microRNAs that target these hub genes. Finally, drug-gene interactions analysis suggests amsacrine, BRD-K68548958, naproxol, palbociclib and teniposide as the top-scored repurposed drugs. The identified biomarkers and pathways might be therapeutic targets to the COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; differentially expressed genes; gene coexpression network; machine learning; protein–protein interaction; systems biology.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Blanco-Melo D, Nilsson-Payant B, Liu W-C, et al. SARS-CoV-2 launches a unique transcriptional signature from in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo systems. bioRxiv 2020. March 24, 2020. doi: 10.1101/2020.03.24.004655 Arxiv biorxiv;2020.03.24.004655v1, preprint: not peer reviewed. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

