The acetabular roof reinforcement plate for the treatment of displaced acetabular fractures in the elderly: results in 59 patients
- PMID: 33839910
- PMCID: PMC9296387
- DOI: 10.1007/s00402-021-03829-9
The acetabular roof reinforcement plate for the treatment of displaced acetabular fractures in the elderly: results in 59 patients
Abstract
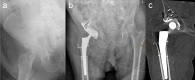
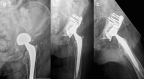
Introduction: Open reduction and internal fixation is considered the gold standard of treatment for displaced acetabular fractures in younger patients. For elderly patients with osteoporotic bone quality, however, primary total hip arthroplasty (THA) with the advantage of immediate postoperative mobilization might be an option. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the clinical and radiological outcomes of surgical treatment of displaced osteoporotic acetabular fractures using the acetabular roof reinforcement plate (ARRP) combined with THA.
Materials and methods: Between 2009 and 2019, 84 patients were operated using the ARRP combined with THA. Inclusion criteria were displaced osteoporotic fractures of the acetabulum with or without previous hemi- or total hip arthroplasty, age above 65 years, and pre-injury ability to walk at least with use of a walking frame. Of the 84 patients, 59 could be followed up after 6 months clinically and radiographically. Forty-nine (83%) were primary fractures and 10 (17%) periprosthetic acetabular fractures.
Results: The mean age was 80.5 years (range 65-98 years). The average time from injury to surgery was 8.5 days (range 1-28). Mean time of surgery was 167 min (range 100-303 min). Immediate postoperative full weight bearing (FWB) was allowed for 51 patients (86%). At the 6-month follow-up, all 59 patients except one showed bony healing and incorporation of the ARRP. One case developed a non-union of the anterior column. No disruption, breakage or loosening of the ARRP was seen. Additional CT scans performed in 18 patients confirmed bony healing. Twenty-six patients (44%) had regained their pre-injury level of mobility. Complications requiring revision surgery occurred in 8 patients. Five of them were suffering from a prosthetic head dislocation, one from infection, one from hematoma and one from a heterotopic ossification.
Conclusions: The ARRP has proven to provide sufficient primary stability to allow for immediate FWB in most cases and represents a valuable option for the surgical management of displaced acetabular fractures in this challenging patient group.
Keywords: Acetabular fracture; Antiprotrusion cage; Elderly; Full weight bearing; Osteoporosis; Reinforcement ring; Total hip arthroplasty.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
H. Resch is registered inventor of a granted patent for the ARRP and is contractual recipient of royalties in case of commercial exploitation. All other authors have no conflict of interest relating to this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Ochs BG, Marintschev I, Hoyer H, Rolauffs B, Culemann U, Pohlemann T, Stuby FM. Changes in the treatment of acetabular fractures over 15 years: analysis of 1266 cases treated by the German Pelvic Multicentre Study Group (DAO/DGU) Injury. 2010;41(8):839–851. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2010.04.010. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

