Patient Perspectives on the Extent of Surgery and Radioactive Iodine Treatment for Low-Risk Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
- PMID: 33840638
- PMCID: PMC10028733
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eprac.2021.01.005
Patient Perspectives on the Extent of Surgery and Radioactive Iodine Treatment for Low-Risk Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
Abstract
Objective: To understand patient perspective regarding recommended changes in the 2015 American Thyroid Association (ATA) guidelines. Specifically, in regard to active surveillance (AS) of some small differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC), performance of less extensive surgery for low-risk DTC, and more selective administration of radioactive iodine (RAI).
Methods: An online survey was disseminated to thyroid cancer patient advocacy organizations and members of the ATA to distribute to the patients. Data were collected on demographic and treatment information, and patient experience with DTC. Patients were asked "what if" scenarios on core topics, including AS, extent of surgery, and indications for RAI.
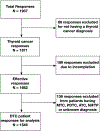
Results: Survey responses were analyzed from 1546 patients with DTC: 1478 (96%) had a total thyroidectomy, and 1167 (76%) underwent RAI. If there was no change in the overall cancer outcome, 606 (39%) of respondents would have considered lobectomy over total thyroidectomy, 536 (35%) would have opted for AS, and 638 (41%) would have chosen to forego RAI. Moreover, (774/1217) 64% of respondents wanted more time with their clinicians when making decisions about the extent of surgery. A total of 621/1167 of patients experienced significant side effects with RAI, and 351/1167 of patients felt that the risks of treatment were not well explained. 1237/1546 (80%) of patients felt that AS would not be overly burdensome, and quality of life was the main reason cited for choosing AS.
Conclusion: Patient perspective regarding choice in the management of low-risk DTC varies widely, and a large proportion of DTC patients would change aspects of their care if oncologic outcomes were equivalent.
Keywords: active surveillance; decision-making; patient perspective; radioactive iodine; survivorship; thyroid cancer.
Copyright © 2021 AACE. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Carrie C. Lubitz: no conflicts of interest to disclose. CCL time and contribution to this work was supported by the NIH/NCI 1R37CA231957-01 (PI)
Colleen M. Kiernan: no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Asmae Toumi: no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Tiannan Zhan: no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Mara Y. Roth: no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Julie A. Sosa: No conflicts of interest. Disclosures: JAS is a member of the Data Monitoring Committee of the Medullary Thyroid Cancer Consortium Registry supported by GlaxoSmithKline, Novo Nordisk, Astra Zeneca, and Eli Lilly.
R. Michael Tuttle: No conflicts of interest. Disclosures: MT contribution to this work was supported by the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Core Grant, P30 CA 008748 (Craig Thompson, PI) and the NCI SPORE in Thyroid Cancer, 5P50 CA172012-04 (James Fagin, PI) Elizabeth G. Grubbs: no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Patient and Provider Perspectives of a Web-Based Intervention to Support Symptom Management After Radioactive Iodine Treatment for Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Qualitative Study.JMIR Form Res. 2025 Mar 19;9:e60588. doi: 10.2196/60588. JMIR Form Res. 2025. PMID: 40106313 Free PMC article.
-
Radioactive iodine ablation post differentiated thyroid cancer surgery: an analysis of use and impact of the American Thyroid Association guidelines.ANZ J Surg. 2019 Nov;89(11):E502-E506. doi: 10.1111/ans.15522. Epub 2019 Oct 31. ANZ J Surg. 2019. PMID: 31674140
-
Comparison between the different doses of radioactive iodine ablation prescribed in patients with intermediate-to-high-risk differentiated thyroid cancer.Ann Nucl Med. 2019 Jul;33(7):495-501. doi: 10.1007/s12149-019-01357-6. Epub 2019 Apr 6. Ann Nucl Med. 2019. PMID: 30955202
-
Current controversies in the initial post-surgical radioactive iodine therapy for thyroid cancer: a narrative review.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2014;21(6):R473-84. doi: 10.1530/ERC-14-0286. Epub 2014 Oct 2. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25277792 Review.
-
Selective use of radioactive iodine (RAI) in thyroid cancer: No longer "one size fits all".Eur J Surg Oncol. 2018 Mar;44(3):348-356. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2017.04.002. Epub 2017 May 3. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2018. PMID: 28545679 Review.
Cited by
-
Lobo-isthmectomy in the management of differentiated thyroid cancer.Thyroid Res. 2023 Feb 13;16(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s13044-022-00145-1. Thyroid Res. 2023. PMID: 36775829 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review: Improving quality of life in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 27;13:1032581. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1032581. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36776310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Controversies in Low-Risk Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Reducing Overtreatment in an Era of Overdiagnosis.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023 Jan 17;108(2):271-280. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgac646. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023. PMID: 36327392 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Nasolacrimal Dysfunction in Thyroid Cancer Survivors.Thyroid. 2022 May;32(5):483-485. doi: 10.1089/thy.2022.0095. Epub 2022 Mar 22. Thyroid. 2022. PMID: 35180829 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The Landmark Series: Extent of Surgery for Low-Risk Differentiated Thyroid Cancer.Ann Surg Oncol. 2025 May;32(5):3119-3125. doi: 10.1245/s10434-025-17063-9. Epub 2025 Feb 26. Ann Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40009309 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Society AC. Thyroid Cancer Statistics Center 2019. [Available from: https://cancerstatisticscenter.cancer.org/?_ga=2.212865491.655297014.156....
-
- Davies L, Welch HG. Current thyroid cancer trends in the United States. JAMA otolaryngology-- head & neck surgery. 2014;140(4):317–22. - PubMed
-
- Wang TS, Goffredo P, Sosa JA, Roman SA. Papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: an over-treated malignancy? World journal of surgery. 2014;38(9):2297–303. - PubMed
-
- Hu G, Zhu W, Yang W, Wang H, Shen L, Zhang H. The Effectiveness of Radioactive Iodine Remnant Ablation for Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. World journal of surgery. 2016;40(1):100–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

