Family-Centered Pediatric Plastic Surgery Care
- PMID: 33840854
- PMCID: PMC8029619
Family-Centered Pediatric Plastic Surgery Care
Abstract
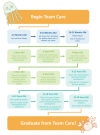
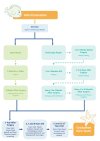
Our multidisciplinary cleft palate and craniofacial center was established in 1978 and manages more than 5,000 active patients from birth to skeletal maturity. Over the past four years we have implemented a complex family-centered reorganization, with the goal of improving care and patient retention. Through our implementation of a familycentered approach, we have also decreased treatment burden, need for secondary procedures and cost of care. 1-12.
Copyright 2021 by the Missouri State Medical Association.
Figures




References
-
- Skladman R, Grames LM, Skolnick G, et al. Adult Quality of Life Post Cleft Palate Repair: A Comparison of Two Techniques. J Craniofac Surg. 2017;28(4):909–14. - PubMed
-
- Padovano WM, Snyder-Warwick AK, Skolnick GB, et al. Evaluation of Multidisciplinary Team Clinic for Patients With Isolated Cleft Lip. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2020;57(7):900–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
