Gintonin facilitates brain delivery of donepezil, a therapeutic drug for Alzheimer disease, through lysophosphatidic acid 1/3 and vascular endothelial growth factor receptors
- PMID: 33841007
- PMCID: PMC8020287
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jgr.2019.12.002
Gintonin facilitates brain delivery of donepezil, a therapeutic drug for Alzheimer disease, through lysophosphatidic acid 1/3 and vascular endothelial growth factor receptors
Abstract
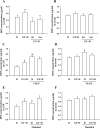
Background: Gintonin is a ginseng-derived exogenous G-protein-coupled lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) receptor ligand, which exhibits in vitro and in vivo functions against Alzheimer disease (AD) through lysophosphatidic acid 1/3 receptors. A recent study demonstrated that systemic treatment with gintonin enhances paracellular permeability of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) through the LPA1/3 receptor. However, little is known about whether gintonin can enhance brain delivery of donepezil (DPZ) (Aricept), which is a representative cognition-improving drug used in AD clinics. In the present study, we examined whether systemic administration of gintonin can stimulate brain delivery of DPZ.
Methods: We administered gintonin and DPZ alone or coadministered gintonin with DPZ intravenously or orally to rats. Then we collected the cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) and serum and determined the DPZ concentration through liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) analysis.
Results: Intravenous, but not oral, coadministration of gintonin with DPZ increased the CSF concentration of DPZ in a concentration- and time-dependent manner. Gintonin-mediated enhancement of brain delivery of DPZ was blocked by Ki16425, a LPA1/3 receptor antagonist. Coadministration of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) + gintonin with DPZ similarly increased CSF DPZ concentration. However, gintonin-mediated enhancement of brain delivery of DPZ was blocked by axitinip, a VEGF receptor antagonist. Mannitol, a BBB disrupting agent that increases the BBB permeability, enhanced gintonin-mediated enhancement of brain delivery of DPZ.
Conclusions: We found that intravenous, but not oral, coadministration of gintonin facilitates brain delivery of DPZ from plasma via LPA1/3 and VEGF receptors. Gintonin is a potential candidate as a ginseng-derived novel agent for the brain delivery of DPZ for treatment of patients with AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer disease; Brain delivery; Donepezil; Ginseng; Gintonin.
© 2020 The Korean Society of Ginseng, Published by Elsevier Korea LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Atypical formations of gintonin lysophosphatidic acids as new materials and their beneficial effects on degenerative diseases.J Ginseng Res. 2024 Jan;48(1):1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2023.02.004. Epub 2023 Feb 21. J Ginseng Res. 2024. PMID: 38223830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gintonin, a ginseng-derived exogenous lysophosphatidic acid receptor ligand, enhances blood-brain barrier permeability and brain delivery.Int J Biol Macromol. 2018 Jul 15;114:1325-1337. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.03.158. Epub 2018 Mar 29. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018. PMID: 29604355
-
Gintonin influences the morphology and motility of adult brain neurons via LPA receptors.J Ginseng Res. 2021 May;45(3):401-407. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2020.06.003. Epub 2020 Jul 21. J Ginseng Res. 2021. PMID: 34025133 Free PMC article.
-
Gintonin, a ginseng-derived novel ingredient, evokes long-term potentiation through N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor activation: involvement of LPA receptors.Mol Cells. 2012 Dec;34(6):563-72. doi: 10.1007/s10059-012-0254-4. Epub 2012 Nov 15. Mol Cells. 2012. PMID: 23161173 Free PMC article.
-
Gintonin: a novel ginseng-derived ligand that targets G protein- coupled lysophosphatidic acid receptors.Curr Drug Targets. 2012 Dec;13(13):1659-64. doi: 10.2174/138945012803529947. Curr Drug Targets. 2012. PMID: 23017203 Review.
Cited by
-
Gintonin enhances epithelial barrier function by activating NRF2 pathway in radiation-induced intestinal injury.J Ginseng Res. 2025 May;49(3):248-259. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2025.01.003. Epub 2025 Jan 19. J Ginseng Res. 2025. PMID: 40453351 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the Role of Autotaxin and Lysophosphatidic Acid in Alzheimer's Disease: From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Potential.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 23;26(15):7068. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157068. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cognitive improvement effect of gintonin might be associated with blood-brain barrier permeability enhancement: dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI pilot study.Transl Clin Pharmacol. 2021 Mar;29(1):21-32. doi: 10.12793/tcp.2021.29.e2. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Transl Clin Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33854998 Free PMC article.
-
Atypical formations of gintonin lysophosphatidic acids as new materials and their beneficial effects on degenerative diseases.J Ginseng Res. 2024 Jan;48(1):1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2023.02.004. Epub 2023 Feb 21. J Ginseng Res. 2024. PMID: 38223830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Active Compounds of Panax ginseng in the Improvement of Alzheimer's Disease and Application of Spatial Metabolomics.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Dec 26;17(1):38. doi: 10.3390/ph17010038. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38256872 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Burns A., Rossor M., Hecker J., Gauthier S., Petit H., Moller H.J. The effects of donepezil in Alzheimer’s disease – results from a multinational trial. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 1999;10:237–244. - PubMed
-
- Jelic V., Darreh-Shori T. Donepezil: a review of pharmacological characteristics and role in the management of Alzheimer disease. Clin Med Insights Ther. 2010;2:771–788.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

