Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome and Lung Disease: Pathogenesis and Therapeutics
- PMID: 33841163
- PMCID: PMC8028140
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.644671
Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome and Lung Disease: Pathogenesis and Therapeutics
Abstract
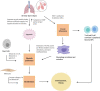
Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome (HPS) is a rare, genetic, multisystem disorder characterized by oculocutaneous albinism (OCA), bleeding diathesis, immunodeficiency, granulomatous colitis, and pulmonary fibrosis. HPS pulmonary fibrosis (HPS-PF) occurs in 100% of patients with subtype HPS-1 and has a similar presentation to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Upon onset, individuals with HPS-PF have approximately 3 years before experiencing signs of respiratory failure and eventual death. This review aims to summarize current research on HPS along with its associated pulmonary fibrosis and its implications for the development of novel treatments. We will discuss the genetic basis of the disease, its epidemiology, and current therapeutic and clinical management strategies. We continue to review the cellular processes leading to the development of HPS-PF in alveolar epithelial cells, lymphocytes, mast cells, and fibrocytes, along with the molecular mechanisms that contribute to its pathogenesis and may be targeted in the treatment of HPS-PF. Finally, we will discuss emerging new cellular and molecular approaches for studying HPS, including lentiviral-mediated gene transfer, induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), organoid and 3D-modelling, and CRISPR/Cas9-based gene editing approaches.
Keywords: hermansky-pudlak syndrome; immunopathogenesis; lung; pulmonary fibrosis; therapeutics.
Copyright © 2021 Velázquez-Díaz, Nakajima, Sorkhdini, Hernandez-Gutierrez, Eberle, Yang and Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ahuja S., Knudsen L., Chillappagari S., Henneke I., Ruppert C., Korfei M., et al. (2016). MAP1LC3B overexpression protects against Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome type-1-induced defective autophagy in vitro . Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 310, L519–L531. 10.1152/ajplung.00213.2015 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- American Thoracic Society, European Respiratory Society (2002). American thoracic society/European respiratory society international multidisciplinary consensus classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. This joint statement of the American thoracic society (ATS), and the European respiratory society (ERS) was adopted by the ATS board of directors, june 2001 and by the ERS executive committee, June 2001,. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 165, 277–304. 10.1164/ajrccm.165.2.ats01 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

