Association Between Lipoprotein (A) and Diabetic Nephropathy in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 33841331
- PMCID: PMC8024696
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2021.633529
Association Between Lipoprotein (A) and Diabetic Nephropathy in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Lipoprotein (a) [Lp (a)] has been well recognized as a risk factor of cardiovascular disease. However, the association between serum Lp (a) and diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) remains unknown. We performed a meta-analysis to comprehensively evaluate the above association.
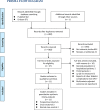
Methods: Observational studies aiming to evaluate the independent association between serum Lp (a) and diabetic nephropathy in T2DM patients were identified by systematic search of PubMed and Embase databases. A random-effect model which incorporated the potential intra-study heterogeneity was used for the meta-analysis.
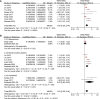
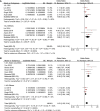
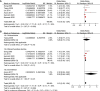
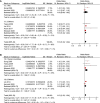
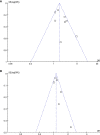
Results: Eleven observational studies with 9304 T2DM patients were included. Results showed that compared to those with the lowest Lp (a), patients with the highest Lp (a) level had higher odds of diabetic nephropathy (adjusted odds ratio [OR]: 1.63, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.25-2.14, I2 = 54%, P < 0.001). Meta-analysis of studies in which Lp (a) was presented as continuous variables showed consistent result (adjusted OR: 1.13 for 1 mg/dl increment of Lp (a), 95% CI: 1.03-1.24, I2 = 36%, P = 0.008). Subgroup analyses showed that study characteristics such as definitions of diabetic nephropathy and study design did not significantly affect the association (P for subgroup difference all > 0.05).
Conclusions: Higher serum Lp (a) in patients with T2DM is independently associated with higher odds of diabetic nephropathy. Large scale prospective cohort studies are needed to validate this finding. Moreover, the potential influence of Lp (a) lowering on renal function in T2DM patients may be further investigated.
Keywords: diabetic nephropathy; lipoprotein (a); meta-analysis; observational studies; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Copyright © 2021 Ren, Zhang and Yan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Can Lipoprotein(a) Predict the Risk of Diabetic Nephropathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus?: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Horm Metab Res. 2025 Apr;57(4):242-251. doi: 10.1055/a-2554-0696. Epub 2025 Apr 10. Horm Metab Res. 2025. PMID: 40209745
-
Serum lipoprotein(a) levels and diabetic nephropathy among Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.J Diabetes Complications. 2016 Jul;30(5):923-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2016.02.006. Epub 2016 Feb 12. J Diabetes Complications. 2016. PMID: 26947887
-
Prospective study of lipoprotein(a) as a risk factor for deteriorating renal function in type 2 diabetic patients with overt proteinuria.Diabetes Care. 2005 Jul;28(7):1718-23. doi: 10.2337/diacare.28.7.1718. Diabetes Care. 2005. PMID: 15983325
-
Lp(a) and Apo-lipoproteins as predictors for micro- and macrovascular complications of diabetes: A case-cohort study.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2020 Sep 24;30(10):1723-1731. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2020.05.011. Epub 2020 May 26. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2020. PMID: 32636121
-
Association Between Serum Irisin and Diabetic Nephropathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis.Horm Metab Res. 2021 May;53(5):293-300. doi: 10.1055/a-1475-4444. Epub 2021 May 7. Horm Metab Res. 2021. PMID: 33962476 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Approaches in Chronic Renal Failure without Renal Replacement Therapy: A Review.Biomedicines. 2023 Oct 18;11(10):2828. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11102828. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37893201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic impacts of diabetes status and lipoprotein(a) levels in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: a prospective cohort study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023 Jun 26;22(1):151. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-01881-w. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023. PMID: 37365608 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated plasma concentrations of lipoprotein (a) are associated with cardiovascular diseases in patients with early-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Apr 30;16:1434745. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1434745. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40370778 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship of liver fat content with systemic metabolism and chronic complications in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Lipids Health Dis. 2023 Jan 24;22(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s12944-023-01775-6. Lipids Health Dis. 2023. PMID: 36694216 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical research on the application of AI-assisted computing systems in the treatment of intermittent exotropia.BMC Ophthalmol. 2025 Jul 28;25(1):432. doi: 10.1186/s12886-025-04240-3. BMC Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40739550 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

