Exaptation Traits for Megafaunal Mutualisms as a Factor in Plant Domestication
- PMID: 33841476
- PMCID: PMC8024633
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2021.649394
Exaptation Traits for Megafaunal Mutualisms as a Factor in Plant Domestication
Abstract
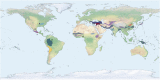
Megafaunal extinctions are recurring events that cause evolutionary ripples, as cascades of secondary extinctions and shifting selective pressures reshape ecosystems. Megafaunal browsers and grazers are major ecosystem engineers, they: keep woody vegetation suppressed; are nitrogen cyclers; and serve as seed dispersers. Most angiosperms possess sets of physiological traits that allow for the fixation of mutualisms with megafauna; some of these traits appear to serve as exaptation (preadaptation) features for farming. As an easily recognized example, fleshy fruits are, an exaptation to agriculture, as they evolved to recruit a non-human disperser. We hypothesize that the traits of rapid annual growth, self-compatibility, heavy investment in reproduction, high plasticity (wide reaction norms), and rapid evolvability were part of an adaptive syndrome for megafaunal seed dispersal. We review the evolutionary importance that megafauna had for crop and weed progenitors and discuss possible ramifications of their extinction on: (1) seed dispersal; (2) population dynamics; and (3) habitat loss. Humans replaced some of the ecological services that had been lost as a result of late Quaternary extinctions and drove rapid evolutionary change resulting in domestication.
Keywords: crops; domestication; ecosystem engineering; endozoochory; exaptation; megafauna; origins of agriculture; seed dispersal.
Copyright © 2021 Spengler, Petraglia, Roberts, Ashastina, Kistler, Mueller and Boivin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Adams C. D., Baker H. G. (1962). Weeds of cultivation and grazing lands, in Agriculture and Land Use in Ghana, ed Wills G. B. (London: Oxford University Press; ), 402–415.
-
- Anderson E. (1949). Introgressive Hybridization. New York, NY: John Wiley.
-
- Anderson E. (1952). Plants, Man and Life. Berkeley, CA: University of California Press.
-
- Anderson E., Stebbins G. L. (1954). Hybridization as an evolutionary stimulus. Evolution 8, 378–388. 10.1111/j.1558-5646.1954.tb01504.x - DOI
-
- Arnold M. L. (1997). Natural Hybridization and Evolution. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

