Histone Deacetylase Inhibitory and Cytotoxic Activities of the Constituents from the Roots of Sophora Pachycarpa
- PMID: 33841520
- PMCID: PMC8019873
- DOI: 10.22037/ijpr.2020.112442.13760
Histone Deacetylase Inhibitory and Cytotoxic Activities of the Constituents from the Roots of Sophora Pachycarpa
Abstract
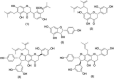
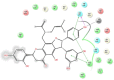
Four prenylated flavonoids, including isosophoranone, sophoraflavanone G, alopecurone J, alopecurone P, and a resveratrol derivative HPD (2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2,3-dihydrobenzo[b] furan-3,4,6-triol), were isolated from the roots of Sophora pachycarpa. The cytotoxic activity of obtained compounds was evaluated against A2780, A549, HeLa, and HCT116 human cancer cell lines. We also evaluated their histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitory activities. Of all compounds tested, alopecurone J was the most active with IC50 values in the range of 9.97-30.91 μM against four cancer cell lines with potent pan-HDAC inhibitory activity (IC50 = 0.08-3.85 μM). Molecular docking experiments of these compounds with HDAC8 displayed potential selective HDAC inhibitory. Molecular docking data showed consistent results in the in-vitro experiments with high selectivity towards HDAC8. The Resveratrol group plays an essential role in HDAC inhibition.
Keywords: Cytotoxicity; Histone deacetylase inhibitors; Molecular docking; Sophora pachycarpa; prenylated flavonoids.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Absolute configuration and anti-cancer effect of prenylated flavonoids and flavonostilbenes from Sophora pachycarpa: Possible involvement of Wnt signaling pathway.Bioorg Chem. 2019 Apr;85:498-504. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.01.051. Epub 2019 Feb 6. Bioorg Chem. 2019. PMID: 30802806
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitory and cytotoxic activities of the constituents from the roots of three species of Ferula.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2019 Jan;22(1):93-98. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2018.34338.8151. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30944714 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel coumarin-based benzamides as potent histone deacetylase inhibitors and anticancer agents.Eur J Med Chem. 2017 May 26;132:42-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.03.024. Epub 2017 Mar 18. Eur J Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28340413
-
Biologically active prenylated flavonoids from the genus Sophora and their structure-activity relationship-A review.Phytother Res. 2019 Mar;33(3):546-560. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6265. Epub 2019 Jan 16. Phytother Res. 2019. PMID: 30652369 Review.
-
Sophora alopecuroides L.: An ethnopharmacological, phytochemical, and pharmacological review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Feb 10;248:112172. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112172. Epub 2019 Aug 20. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31442619
Cited by
-
Phytochemistry and pharmacology of natural prenylated flavonoids.Arch Pharm Res. 2023 Apr;46(4):207-272. doi: 10.1007/s12272-023-01443-4. Epub 2023 Apr 14. Arch Pharm Res. 2023. PMID: 37055613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Prenylated Flavonoids of the Fabaceae Family in Medicinal Chemistry: An Updated Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 4;25(23):13036. doi: 10.3390/ijms252313036. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684747 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bolden JE, Peart MJ, Johnstone RW. Anticancer activities of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. . 2006;5:769–84. - PubMed
-
- Kumboonma P, Senawong T, Saenglee S, Yenjai C, Phaosiri C. New histone deacetylase inhibitors from the twigs of Melanorrhoea usitata. Med. Chem. Res. . 2018;27:2004–15.
-
- Zhou Zh, Yang J, Kong AN. Phytochemicals in traditional Chinese herbal medicine: Cancer prevention and epigenetics mechanisms. Curr. Pharmacol. Rep. . 2017;3:77–91.
-
- Khan N, Jeffers M, Kumar S, Hackett C, Boldog F, Khramtsov N, Qian X, Mills E, Berghs SC, Carey N. Determination of the class and isoform selectivity of small-molecule histone deacetylase inhibitors. Biochem. J. . 2008;409:581–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
