Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Infections after Aesthetic Procedures: Comparison of Clinical Features and Treatment
- PMID: 33841617
- PMCID: PMC8021410
Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Infections after Aesthetic Procedures: Comparison of Clinical Features and Treatment
Abstract
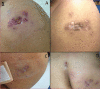
Nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) have been increasingly identified as causative of numerous cosmetic procedure related infections worldwide. This manuscript reports clinical aspects and antimicrobial resistance profiles of NTM infections associated with aesthetic procedures diagnosed in a private infectious disease clinic in the Brazilian Amazon. Four patients developed skin and soft tissue infections between August 2015 and August 2019. Clinical, microbiological, and epidemiological data were collected. M. conceptionense, M. abscessus and M. fortuitum were isolated. The histopathology showed dermal granulomatous inflammation. All patients were treated with a combination of antimycobacterial regimens, mainly with moxifloxacin and clarithromycin.
Keywords: Nontuberculous mycobacteria; aesthetic procedures; treatment.
Copyright © 2020. Matrix Medical Communications. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
FUNDING:No funding was provided for this study. DISCLOSURES:The authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to the content of this article.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
