OX40 as a novel target for the reversal of immune escape in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 33841630
- PMCID: PMC8014382
OX40 as a novel target for the reversal of immune escape in colorectal cancer
Abstract
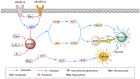
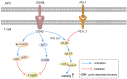
First-generation immunological checkpoint inhibitors, such as CTLA-4, PD-L1 and PD-1 exhibit significant advantages over conventional cytotoxic drugs, such as oxaliplatin and 5-FU, for the treatment of colorectal cancer. However, these inhibitors are not ideal due to their low objective response rate and the vulnerability of these treatment methods when faced with emerging drug resistant cancers. This study summarizes the immunological characteristics of colorectal cancer treatment, and analyzes the ways in which OX40 may improve the efficacy of these treatments. Activation of the OX40 signaling pathway can enhance the activity of CD4+/CD8+ T cells and inhibit the function of Treg. Simultaneously, OX40 can directly inhibit the expression of Foxp3, affect the inhibitory function of Treg, and inhibit the immunosuppressive factors in the tumor microenvironment so as to reverse immune escape and reverse drug resistance. Therefore, OX40 is an important target for treating colorectal cancer in "cold tumors" with less immunogenicity.
Keywords: OX40; colorectal cancer; immune escape; microenvironment.
AJTR Copyright © 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
