Synergistic anti-tumor effect of anti-PD-L1 antibody cationic microbubbles for delivery of the miR-34a gene combined with ultrasound on cervical carcinoma
- PMID: 33841635
- PMCID: PMC8014418
Synergistic anti-tumor effect of anti-PD-L1 antibody cationic microbubbles for delivery of the miR-34a gene combined with ultrasound on cervical carcinoma
Abstract
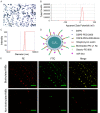
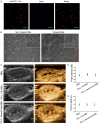
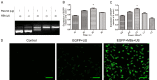
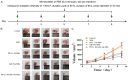
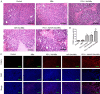
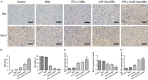
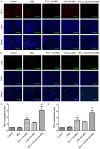
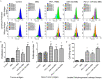
This study explored the synergistic effect of anti-PD-L1 antibody cationic microbubbles (MBs) for delivery of the miR-34a gene combined with ultrasound in inhibiting the cervical cancer. H&E stain, TUNEL, immunohistochemistry and RT-PCR were used to detect the change of apoptosis regulatory factors, and immunofluorescence, Flow cytometry and LDH assays were applied to evaluate the changing of immunomodulatory. In this experiment the PD-L1 Ab/miR-34a-MBs were prepared successfully. The cell targeting assay showed that U14 cells were surrounded by the PD-L1 Ab/miR-34a-MBs and microbubbles had well contrast imaging capability in vivo. With the irradiation power was 1 W/cm2 and the irradiation time was 25 s, the gene transfection efficiency was the highest using EGFP plasmid lorded microbubbles. In vivo anti-tumor assays, the PD-L1 Ab/miR-34a-MBs showed a great potential in inhibiting tumor growth with a TGI of >50%. PD-L1 Ab/miR-34a-MBs treatment enhanced the anti-tumor effect compared with that induced by PD-L1 Ab or miR-34a alone. Firstly, PD-L1 Ab/miR-34a-MBs could gather miR-34a with high-concentration aggregation and releasing around the cervical cancer, which takes a significant role in promoting apoptosis by downregulated Bcl-2 and upregulated Bax. Furthermore, combination therapy was found to augment the activation of T lymphocytes proliferation and increase CD8+ T cells infiltration, to enhance antitumor immune killing effect. The anti-PD-L1 antibody microbubbles for delivery miR-34a gene with ultrasound were considered to be a promising combination therapy regimen via initiating apoptotic mechanism of the tumor and anti-tumor immune regulation.
Keywords: Ultrasound; anti-PD-L1 antibody; cervical cancer; miR-34a; microbubbles.
AJTR Copyright © 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Couzin-Frankel J. Breakthrough of the year 2013. Cancer immunotherapy. Science. 2013;342:1432–1433. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
